
 Founded in the mid-1940s in Fullerton, California by Leo Fender, the legendary amps produced by this company have been heard on countless recordings and are influential on countless other amp makers. In the beginning Fender paired small combo amps with lap steels and electric guitars aimed at student players, but word of the superior tone and build quality quickly spread among professional musicians. In over seventy years of existence, Fender has consistently evolved and innovated its sound from the Tweed era through the Brown and Blackface eras and beyond.
Founded in the mid-1940s in Fullerton, California by Leo Fender, the legendary amps produced by this company have been heard on countless recordings and are influential on countless other amp makers. In the beginning Fender paired small combo amps with lap steels and electric guitars aimed at student players, but word of the superior tone and build quality quickly spread among professional musicians. In over seventy years of existence, Fender has consistently evolved and innovated its sound from the Tweed era through the Brown and Blackface eras and beyond.
Mercury Magnetics has built a massive collection of ToneClone® Transformers and Chokes for Fender Amps available from all eras of production. Answering the needs of players and amp-builders alike, our extensive catalog of audio transformers is the ultimate resource whether you’re looking to replace a worn-out transformer in a vintage Fender amp or looking to nail a vintage tone in a new amp or amp build. The engineers at Mercury have painstakingly documented every detail and nuance of the best-of-breed vintage transformers and can faithfully produce perfect clones using the same materials and methods used on the originals.
The ToneClone+ Series from Mercury Magnetics adds more utility and options without altering the original tone. Love your amp but want to change your speaker configuration? Mercury’s ToneClone+ Output Transformers give players more impedance options like alternate and multi-tapped secondaries. Power Transformers can benefit from the “Plus” treatment as well with alternate primary voltage, Higher or Lower B+ Voltages, added current capability, and more.
 Fender Woodie Amp Transformers: The earliest production amps to come out of Fullerton, Fender ‘Woodie’ amps can be identified by their hardwood cabinets and fixed handles. We are proud to offer ToneClone® transformers from this short-lived and rare Woodie era including the Woodie Deluxe (aka Model 26) and Woodie Pro.
Fender Woodie Amp Transformers: The earliest production amps to come out of Fullerton, Fender ‘Woodie’ amps can be identified by their hardwood cabinets and fixed handles. We are proud to offer ToneClone® transformers from this short-lived and rare Woodie era including the Woodie Deluxe (aka Model 26) and Woodie Pro.
Fender Tweed Amp Transformers: The Fender Tweed era lasted from the late forties to early sixties and a vast  amount of artists from all generations have crafted their distinct tone using these amps through all genres. Notable artists include: Scotty Moore (Elvis Presley), Neil Young, Larry Carlton, Eric Clapton and Keith Richards. Mercury Magnetics has the largest catalog of vintage-correct Fender ToneClone® replacements transformers for the following models: Tweed Bandmaster, Tweed Bassman, Tweed Champ, Tweed Harvard, Tweed Princeton, Tweed Pro/Dual Professional, Tweed Super, Tweed Tremolux, Tweed Deluxe, Tweed Twin, and Tweed Vibrolux.
amount of artists from all generations have crafted their distinct tone using these amps through all genres. Notable artists include: Scotty Moore (Elvis Presley), Neil Young, Larry Carlton, Eric Clapton and Keith Richards. Mercury Magnetics has the largest catalog of vintage-correct Fender ToneClone® replacements transformers for the following models: Tweed Bandmaster, Tweed Bassman, Tweed Champ, Tweed Harvard, Tweed Princeton, Tweed Pro/Dual Professional, Tweed Super, Tweed Tremolux, Tweed Deluxe, Tweed Twin, and Tweed Vibrolux.
Fender Blonde and Brown (Brownface) Amp Transformers: Sitting on the timeline between the Tweed and Blackface Fender amps, the Blonde/Brown amps of the early sixties were most noticeably embraced by surf groups like the Beach Boys and Dick Dale. Our catalog of ToneClone® amp transformers for this era includes Brown/Blonde Bandmaster, Blonde Bassman, Blonde Showman, Blonde Tremolux, Blonde Twin, Brown Concert, Brown Deluxe, Brown Princeton, Brown Pro, Brown Super, Brown Vibrasonic, Brown Vibrolux, and Brown Vibroverb. Also see our transformers and choke for the 6G15 Reverb Unit.
 Fender Blackface Amp Transformers: Easily distinguishable by their black control plates and white lettering, Fender Blackface amps began showing up on stages and recordings in the early-mid 1960s. Extremely popular among musicians then, the impressive build quality and versatile tones have kept these classic amps popular even 50 years later. Mercury Magnetics has hundreds of ToneClone® and ToneClone+ transformers and chokes for Fender Blackface Amps including: Blackface Bandmaster/Bandmaster Reverb, Blackface Bassman, Blackface Champ, Blackface Concert, Blackface Deluxe/Deluxe Reverb, Blackface Princeton/Princeton Reverb, Blackface Pro/Pro Reverb, Blackface Showman, Blackface Tremolux, Blackface Twin Reverb, Blackface Vibrochamp, Blackface Vibrolux, and Blackface Vibroverb. Also see our transformers and choke for the 6G15 Reverb Unit.
Fender Blackface Amp Transformers: Easily distinguishable by their black control plates and white lettering, Fender Blackface amps began showing up on stages and recordings in the early-mid 1960s. Extremely popular among musicians then, the impressive build quality and versatile tones have kept these classic amps popular even 50 years later. Mercury Magnetics has hundreds of ToneClone® and ToneClone+ transformers and chokes for Fender Blackface Amps including: Blackface Bandmaster/Bandmaster Reverb, Blackface Bassman, Blackface Champ, Blackface Concert, Blackface Deluxe/Deluxe Reverb, Blackface Princeton/Princeton Reverb, Blackface Pro/Pro Reverb, Blackface Showman, Blackface Tremolux, Blackface Twin Reverb, Blackface Vibrochamp, Blackface Vibrolux, and Blackface Vibroverb. Also see our transformers and choke for the 6G15 Reverb Unit.

We told this was coming.. Tes, when readers ask us to review something, we do our best to respond, and thanks to RedPlate founder Henry Heistand, we received two RedPlates for review. We’ll start this episode by telling you that Henry Heistand appears to be a very clever fellow who is not working in the shadows of that past, which is to say that he builds feature-rich amplifiers that in no way pretend to be vintage knock-offs. Play a RedPlate and you’re firmly treading in the present, rather than mining tone out of a dusty box built by a dead man (or woman—sorry Lily). And that’s fine. There is certainly ample space in these pages for the living, and RedPlates are in fact very lively tools indeed. We asked Henry to give us a glimpse into his background and motivation, and our reviews of the TweedyVerb and BlackVerb follow….
TQR: How and when did you initially become involved in electronics and amplification?
HH: Starting around age 12 playing to the radio and jamming with friends, my first build attempt was a speaker cabinet made out of ½ plywood and covered with yellow carpeting. It had a leopard (spotted) grill cloth and contained 6 speakers recycled from various old TVs and stereos. My first real amp repair was replacing a screen resistor in a Fender Bassman in 1970. I went to college for a year and then played guitar full time until 1979 when I attended electronics school (they still taught tubes). To pay for school I got a part time job at a church organ repair shop that had a “combo” repair department and still played in club bands on weekends. Attending electronics school in the morning and repairing gear in the afternoons was a great way to instantly translate the classroom to the real world. Compared to the tube TVs and tube broadcast transmitters, the tube musical amplifiers were relatively simple. Besides Fender and Marshall, tube amps by Sunn, Ampeg, Gibson, West, Park, Hiwatt, Sound City and all the Supro/Kalamazoo/Dan Electro stuff. If I only had a nickel for every good tube I tossed in the trash back then. Many of those same companies had solid-state amps too along with companies like Acoustic, Kustom, Peavey, Randall, Lab, SG and Roland. It seems like the ’70s was the golden era of guitar amp designers. Although most tube amps have a similar topology, the differences between brands in those days ranged from truly innovative to laughable. On a few occasions when a solid-state repair would come in that was totally fubar, one of the church organ repair guys would show me how to design a new circuit right over the top of the problem area, teaching me the value of having a few simple circuit designs at the ready for emergencies. In late ’82 I got a career job in the computer field, and by ’86 purchased the part of the church organ repair shop that repaired the “combo” gear. The new company was named Music Mechanix and kept the warranty contracts with all the majors for amps, keyboards and P.A.s.
TQR: As you became more familiar with various amp designs of the past, what were your favorites and why?
HH: Thinking back to the tonal memories accumulated during those years spent repairing amps, the most musical of all of them were probably the early ’60s Fender tube amps. In addition to repairs, Music Mechanix did all the popular mods of the day (anyone remember the original Train Wreck Mod pages for Fenders?), many times we would redo almost everything inside but keeping the exterior unchanged. Most of my playing back then was strictly radio cover songs so the quest was always to find the one amp that could imitate everything. Music Mechanix was continuing the warranty station status from the previous owner (established in the ’50s) so every original manufacturer’s amplifier schematic ever released was available as a reference source, residing in 16 large file cabinets. On the side, I kept a little notebook of circuits and mods of interest to use as building blocks.
TQR: Can you describe the lasting impressions created by your study of the experiences with classic amps that have most affected your own design philosophy and preferences?
HH: As a service to friends and regular customers Music Mechanix would take a classic amp (at the time it was easy to get something like a used Bassman for $100) and do Frankenstein amps that were Fender this, Marshall that, with a sprinkling of Vox and Ampeg thrown in depending on the customer’s needs. On the weekends I was doing gigs using a pair of modified Ampeg VT-40s in stereo until somehow I ended up with a Mesa Boogie S.O.B. that had a really innovative phase inverter section controlled by a “LIMIT” knob. A bizarre variation of a PI section’s constant current source, the circuit was not in the RCA manual or on any other schematic. It sparked something in me and from hen on I started doing creative amp mods that were not copies of things I had seen on schematics.
TQR: When did you first begin to sketch out the concept for RedPlate amps, and what did you want to accomplish that would be unique and different?
HH: I had always been fascinated with “sleeper” amps that looked small but sounded big. After selling the repair business I used my free time to do a lot of experimentation on point-to-point builds in a Fender Camp sized chassis, eventually working out how to do a 7 tube, large transformer build in a Champ chassis without noise or oscillation. My favorite guitar tones were the recorded sounds of the Mesa Boogie/Dumble ODS type amps (even before I even knew what a Dumble amp was). A clean singing tone with a hint of character that sustains and blooms is my idea of the ultimate tone and the design goal of all the RedPlate models.
TQR: Can you briefly describe the unique features and differences among the current line of RedPlate models?
HH: RedPlate probably has too many models because we treat the sections as modular building blocks. We start with one of the 3 chassis sizes:
CH1. 15” width with four 9 pin sockets and two 8 pin sockets, transformers up to the 50 watt size.
CH2: 17” width with six 9 pin sockets and two 8 pin sockets, transformers up to 80 watt size.
CH3: 19” width with five 9 pin sockets and four 8 pin sockets, transformers up to 160 watts
Then we use different combinations of the building blocks with the only limitation being the number of controls (physical knob space) and the number of tube sockets available. Building blocks currently in use:
BB1. PREAMP1—Tweed—A single tone knob preamp (Tweed style).
BB2. PREAMP2—Blackface—A Treble, Middle, Bass Preamp (Blackface style).
BB3. DRIVE1—A three knob overdrive section (Gain, Drive, and Level).
BB4. DRIVE2—A six knob overdrive section (Gain, Drive, Level, Treble, Middle and Bass).
BB5. REVERB—A single knob tube reverb with medium decay tank.
BB6. EFFECTS LOOP—A fully buffered serial loop, return level is the master volume.
BB7. PHASE INVERTER—Standard Long Tail pair, very similar to the early ’60s designs.
BB8. POWER AMP #1—40 watts cathode bias (6L6GC).
BB9. POWER AMP #2—50 watts fixed bias/40 watts cathode bias (6V6GC)
BB10. POWER AMP #3—80 watts fixed bias (KT-88).
BB11. POWER AMP #4—45 watts fixed bias/18 watts cathode bias (6V6GTA)
BB12. POWER AMP #5—100 watts fixed/50 watts fixed (6L6GC).
TQR: Both of our review amps are loaded with Warehouse speakers from Kentucky, which we have reviewed before. How extensive are your evaluations of various speakers when creating a new model? Does the same process apply with transformers, tubes or other components?
HH: The current lineup is using WGS Retro 30, WGS British Lead 80 and Eminence Swamp Thang speakers in the combo amps. The decision to use these was based on side-by-side comparisons with other brands (an ongoing process).
Tube selection is mostly based on reliability (as long as the tone is still there). The current production amps use Svetlana 6L6GC, SovTek 12AX7LP (PI tube), and Electro Harmonix 6V6GTA and 12AX7s (preamp).
Selecting individual signal path components is more difficult because side-by-side comparisons can be misleading (no 2 amps are exactly alike). The signal path in current production amps use PS series Orange Drop capacitors and carbon film resistors based on low noise and musical warmth in the tone. RedPlate Amps has a good relationship with Mercury Magnetics and I like to use their transformers in most models.
TQR: How does the half power switch function in your amps, as well as the “mode” control and various voicing controls?
HH: Depending on the output section, 3 methods are used:
1. 6L6GC 100 watt/50 watt—The switch lifts two of the four tubes by 10K so they are effectively out of the circuit yet the impedance selection is still valid.
2. 6V6GTA 45 watt/18 watt—Full power runs two of the tube in cathode bias and two in fixed bias, the switch lifts the fixed bias tubes by 10K to effectively remove them without changing the output impedance.
3. 17 Watt (Hi/Lower)—This switch just lowers the voltage to the phase inverter tube so the amp breaks up sooner. There are two different styles of mode switches. On the Tweed style preamps the 6 position mode regressively reduces midrange and preamp output to imitate a Blackface style amp. On the Blackface style preamp the 6 position mode switch progressively fattens the midrange to imitate a Tweed style amp. Most of the models also include a Humbucking/single coil switch to set the amount of bass gain in the input stage.
TQR: How much individual customization or voicing do you offer for specific models when working with an artist?
HH: Unlimited customization is available, although most of the professionals that use RedPlate Amps are content playing standard models.
TQR: We noticed that you include the owner’s name on the back panel, correct? A nice touch…
HH: Yeah, the front and rear panels are done in-house, we could even put pictures of your dog on there.
TQR: What do you want to accomplish in the future? New models?
HH: “Amps that sing” being every guitar player! Going forward, curiosity and customer feedback will continue to drive the evolution of current designs and the development of new designs. For example, there will be a “shredder” amp in the near future (The ShredPlate) and possibly a bass amp. As RedPlate continues to gain name recognition with the music industry, models like the BlackVerb, MagicDust and TweedyVerb will hopefully be taken for granted as standard amplifier types.
The front and rear panels on the BlackVerb reveal an impressive array of controls, push/pull-knobs and switched pots. In fact, the printed operation guide includes a signal path diagram on the front page with a welcoming invitation to skip an in-depth review of the manual and just set all the knobs at 12 noon and play, which we did, consulting the manual as needed as we spent more time with the amp. So, is the BlackVerb too complicated for you “plug & play” guys? Not really, but the control panel is best reviewed in sections. You’re essentially working with a clean preamp circuit and a Drive section that includes Gain, Drive and Level controls for variable levels of distortion overdriven tones, but there are still many more additional tweakable features lurking within…
The first control adjacent to the single front input jack is the miniature Bright switch toggle with the center position OFF, Down producing the sound of “new strings” (an accurate description we might add), and Up rendering a brighter tone that will be familiar to those of you with a Fender Blackface amp with bright switch. We usually use the bright switch to put a little extra shimmer and spank on humbucking pickups, or neck pickups on single coils.
The Volume control includes a pull switch to engage a midrange boost that increases upper mids. The Middle control does what you’d expect, with a pull switch for a “Deep” setting that scoops mids and boosts bass frequencies—an excellent change-up for clean tones. The Bass control handles low end quite well, and it can be clicked OFF to be removed from the tone stack. Try that with a neck pickup and it produces the odd and very different EQ found in some old Valco and Gibson amps.
The Mod Selector is a 6-position rotary EQ switch that gradually produces a fatter, thicker tone as you rotate left to right from the “Funk” setting, to “Normal” and “Fat” (tweed). All this pulling and turning may sound complicated, but you’ll have it thoroughly digested in 5 minutes, and most importantly, these extra EQ controls expand the tonal capabilities of the BlackVerb in a clever and creative way that really is worth using and exploring. We have bitched about such bells and whistles on other amps having limited value, but no such questionable affectations plague the BlackVerb. Like we said, Henry is a clever fellow. On the Drive section…
This is where you mine and manage overdriven tones and distortion. The Gain control can be bypassed by clicking fully left, otherwise, you’re setting the amount of signal being sent to the first gain stage, which produces variable levels of smooth growl and grunt. The Drive control further ramps up distortion through two gain stages, and a pull switch on the knob serves as an afterburner for maximum burn and rip. At this point you will be channeling Metallica at full husky, so hide the dog. The Level control sets the output volume for this section, resulting in a progressively bigger, thicker, bolder voice. Of course, the big selling point for the BlackVerb is how all of your clean, moderately busted up and filthy dirty tones can be deftly tweaked and the volume managed with the Volume and Master volume controls. At the full power setting, you really can get this thing to sound like a 100 watt high gain amp on “7” at low decibel levels suitable for home recording and friendlier sound pressure levels.
The reverb control is what it is, and you can turn it off fully left and it’s out of the circuit. The Presence control is described as using “global negative feedback to remove low frequencies which frees up bandwidth for more midrange and highs,” and it can also be turned off when rotated fully left. Frankly, the appeal of this control escaped us, but we can imagine how it might be useful in a live situation where you may want to avoid too much low end muddying up the mix with bass and drums. The Master volume works very well without producing the dreaded master volume/low volume faux zizzz when you’re trying to light a fire at low volume levels.
One of our favorite features is the 50 watt/40 watt switch on the back panel that changes the boas from fixed to cathode for a completely different feel. With the 40 watt cathode biased setting you can also change the 6L6 output tubes to 6V6s, transforming the BlackVerb into an 18 watt cathode biased flame thrower, or bypassing the Gain section for a more tweedy character and voice. The Hi/Lo power switch changes the voltage on the input stage and the threshold for clean headroom.
The back panel Smooth switch is just that, adding slight compression in the clean preamp, and the Humbucker/Single Coil setting sets the amount of bass gain in the input stage, relieving you of perhaps resetting EQ when switching from single coils to humbuckers.
Additional utilitarian features on the back panel include a handy bias adjustment and test point, speaker impedance selector, main and extension speaker jacks, FX send and return, and footswitch jack. The footswitch gives you the capability to get in and out of the Tweed, Drive and Boost circuits. Tweed boosts upper mids while lifting the midrange control on the front panel for maximum push in the frequencies where the guitar really lies on stage. Drive engages the Drive feature, bypassing it when off at the footswitch. Boost makes everything sound bigger with a partial tone stack lift.
And now for the bottom line…. It seems to us that the intention of the BlackVerb is to be as tonefully versatile as a 1×12 combo amp can possibly be whether you are playing small clubs, bigger rooms or wide open outdoor stages. You could play nothing but smooth, clean jazz through this amp without ever venturing into the gain stages and be perfectly happy. Or you could do nothing but feast off the considerable gain and distortion lurking in the heart of the BlackVerb and be equally happy. Most gigging musicians want to range between such extremes living somewhere in the middle, and you can do that, too. Like most feature-rich amplifiers, you’ll find certain favorite settings that will be revisited with specific guitars, and after a few days you’ll have no trouble quickly accessing those settings, although the control panel is a bit difficult to read until you no longer need to read it at all.
The standard Warehouse Retro 30 speaker is a brighter version of the Veteran 30 we have favorably reviewed in the past. Given the considerable range of overdrive and distortion available in the BlackVerb, the Retro 30’s clear, articulate character and exceptional capacity to handle low frequencies makes it an excellent choice for this amplifier. Even at extreme gain and drive settings, the BlackVerb produces a rich and musical burn that does not mask or obscure essential overtones and harmonics. The clean tones are equally strong, powerful and clear, and the amp will nimbly spill into overdrive played clean at higher volume levels that can be managed with the volume on the guitar. The BlackVerb impressed with its ability to embody many different styles of amplifiers in one compact box, limited only by your capacity for experimentation and your imagination. Imagine that.
We were particularly anxious to experience the TweedyVerb because it seems to fit the power and volume requirements of so many players today, and it is a very straightforward and versatile 1×12 combo that is a breeze to hump to the next gig. Got your attention there, did we? We finally figured out why vintage blackface Pro Reverb amps have remained relatively underpriced… just pick one up.
The TweedyVerb is a cathode biased dual 6L6 amp with reverb, loaded with an 80 watt Warehouse British Lead 12” speaker. You won’t find a bad tone in this amp, and the controls are very intuitive, delivering outstanding “blackface,” “brown” and “tweed” tones via a 6-position Mode switch. The Bright switch is identical to the BlackVerb (you’ll love the “new strings” setting), with a single Volume control, simple Gain control, and a Tone control that can be clicked off fully left to bypass the tone stack for a very heavy and thick does of overdriven tones with excellent dynamic feel and touch sensitivity. The spring reverb is good—delivered form an original new old stock Accutronics pan made by Cary, IL, and the Presence control is identical to the BlackVerb, using global negative feedback to remove low frequencies and emphasize mids and highs. It also seems to decrease volume and gain, best used in our opinion for clean tones.
The 40 watt/17 watt switch on the back panel changes the voltage on the phase inverter. We preferred the sound and girth of the 40 watt setting, which still allows plenty of room for managing volume and variable distortion with the Gain and Volume controls, but the 17 watt setting is fine, too for close quarters. 6V6 power tubes can also be used at this setting without re-biasing for lower power output and volume. A footswitch is included to access both the fat Tweed setting on the Mode switch on the fly, and the Boost function, which acts as a tone stack bypass. Despite its compact size and relatively light weight, the TweedyVerb is a big-sounding amp that produces outstanding clean tones at usable stage volume, yet it can also be gradually pushed into the familiar sound of a Deluxe Reverb on “6” or even a vintage Marshall head at higher volume and gain settings. It’s a right fair chameleon, this one.
The Warehouse 80 watt British Lead 12 gracefully handles the power output of the TweedyVerb with excellent clarity, sold bass, vivid mids and a sweet and chimey top end. Like the BlackVerb, the TweedyVerb offers the sound and feel of several distinctively different amps in one box via the Mode switch, and we liked them all, from the rough and tumble Tweed, the slightly less raucous, smooth upper mid voice of the Brow, and the more scooped, open and airy Black settings. Both RedPlate models reviewed here clearly share the same DNA, which is to say that they possess a remarkably rich and music character, whether you choose to stroke big clean tones through them or dial up a tone that would make Billy Gibbons proud. Douse that light, and Quest forth….

Finding and restoring old amps and cabinets is a slow process that demands patience. From the time we first began trolling eBay, ultimately scoring a tweed Vibrolux and Tremolux, to final delivery of the aged cabinets and assembly of the amps, six months had easily passed.
We first found and bid on a ’58 Vibrolux in September ’06. Sold by an eBay seller in Texas, it had been recovered in reddish-brown cloth similar to the stuff used to cover hymnals or a bad ’60s pleather recliner for the double-wide. Otherwise, it was pretty straight, with the original blown Jensen P10R intact, and the original transformers, caps and resistors. The inside of the cabinet had been painted black, but the cabinet, grill cloth, baffle and control panel were otherwise intact, and the wooden tremolo footswitch was included. We bought the Vibrolux for $1,590.00 with 4 bids placed.
Inspired by Larry Cragg’s detailed description of Neil Young’s tweed Tremolux, a1958 Tremolux surfaced on eBay in November 2006, and we scored it for just $1,082.00 from a seller in San Francisco. We suppose this amp was so cheap because the output transformer had been replaced, and the cabinet had been completely stripped and stained mahogany brown. The original speaker mounting screws in the baffle board were about to fall out. However, the original Tremolux circuit was well-preserved, and a small strip of tape remained in the chassis signed in a delicate hand by “Lilly” – one of the many women in Fullerton employed to assemble amplifiers like the Tremoluxin 1958. God bless her. The Tremolux also arrived with the original wooden foot switch.
The Vibrolux kicked some serious tail right out of the box. We send the original Jensen P10R to John Harrison at A Brown Soun (www.abrown.com) for a re cone, mounting a1965 Jensen C10Q sent by Larry Pogreba in its place – a very stout choice and original equipment in early blackface Vibrolux Reverb amps. Like the Tremolux, the tremolo circuit in the Vibrolux required some TLC,with four caps needing replacement to restore the swampy oscillator circuit to full wobble-weave. We also replaced all the newish tubes with NOS RCAs, Philips and GEs. Once we had the amp mounted in the restored and aged cabinet, we were throwing down hard with our No caster nightly, wallowing in the big sound coming from such an innocent-looking little biter, when the original output trans-former gave it up in a final, glorious gasp. A quick call to Mercury Magnetics produced a ToneClone replacement within a week and we were soon back in business,sounding better than ever.
The 10 watt, 3-input ’58 5F11 Vibrolux is housed in the same cabinet Fender used for narrow panel tweed Deluxe– a fat little featherweight with greasy tremolo and a smooth bark tailor made for a Telecaster. And 10 watts may be the perfect power notch for low-volume home recording and jamming – crystal clear, bright and drenched in gorgeous Fendery overtones at low volume (3-5), and absolutely on fire from 7-10. In all respects, the 5F11 Vibrolux is a big amp in a small package worth pursuing for its outstanding tone and personality at truly usable volume levels.
We were amazed by how Gregg had managed to remove every trace of black paint that had been sprayed inside the cabinet, and his aging job, complete with three coats of amber stain and lacquer, faint water stains along the bottom,worn seams and corners, aged L&L leather handles and scorch marks from the power tubes on the inside of the back panel were flawlessly conceived and applied. Hopkins even recreated the original tube chart with a 1958 date code after requesting that we send him the chassis number and power transformer EIA code for production verification. When we brought the restored Vibrolux to Jeff Bakos’ shop (www.bakosampworks.com), he looked it up and down as it sat on the floor of his workshop, peered into the back and said, “That is totally sick.”
The ’58 Tremolux provided a further study in what can be involved buying 40 year-old amps. Upon arrival,the amp was really smokin,’ even with the Jensen hangin’ off the baffle board. The tremolo was DOA, however, so while the stripped cabinet was getting the spa treatment in St. Louis, Jeff replaced two caps in the trem circuit, we replaced the already replaced output transformer with another from Mercury Magnetics, and stored the chassis away until we received the finished, aged Tremolux cabinet from Gregg in late March ’07.
The 5E9A (’55-’56) and 5G9 (’57-’60) Tremolux are housed in the same taller, wider cabinet Fender used for the 1×15 narrow panel tweed Pro,and the later 5G9 circuit is quite different from both the 5E3 Deluxe and the ’55 5E9ATremolux, being fixed rather than cathode biased, employing a long-tailed phase inverter common to the bigger narrow panel tweed amps, and the addition of an extra filter cap and choke enabled the power to be increased from 15W to 18W in 1957.
Compared to the narrow panel tweed Deluxe and the 5E9 Tremolux, the 5G9 Tremolux develops more volume and headroom, and should you chose to replace the 12AY7 preamp tube with a 12AX7, gain is further increased (it’s already righteous with the 12AY), while the bigger 10” x22” x 10” cabinet produces a much rounder, warmer tone with superior ambience and presence. In the month or so since we’ve had the Tremolux put together in the restored cabinet, a new Tung Sol6V6 blew (after we had opted not to use a couple of spare ’50s RCAs for safety – they are in the amp now and killin’ us with bogs of good thang),and we just took the amp back to Jeff when it began spitting some nasty distortion provoked by low frequencies from the guitar. Turned out to be a few bad solder joints.
Like the Vibrolux, Gregg had stopped short of creating a “3-legged dog with an eye patch,” taking the aging to a moderate level with frayed edges and seams on the amber tweed, a single beer can ring on the top with a foam overflow stain running down the grill cloth, a slight orange stain on one side from pine knot bleed, and assorted scuffs and light abrasions. He also repaired the baffle-board, filling in the old holes for the speaker mounting screws.
We hate doing this to you (again), but truth be told, we have to give the nod to the Tremolux as the most toneful and inspiring amp in its power class (18 watts)that we have ever heard or owned. It’s ascension to Numero Uno status was a bit of a surprise, but then again, we considered the initial source of our inspiration for finding one – Neil Young, via his tech, Larry Cragg, and in hindsight we should have expected as much. With all the attention paid to the tweed Deluxe as the big time bonerizer of the tweed family, the Tremolux seems to have been overlooked for the usual reasons…. In the nose-to-butt-crack daisy-chain march to mediocrity, the masses never seem to acquire a view beyond the first lazy dumb-ass directly in front of them. In the immortal words of the great hoosier educator and smack-down artist Earl Dosey, they are “stepping’ over dimes to pick up nickels.” Let’s hope the lemmings continue to keep their heads down.
So here’s the move…. Sad as we are to share this, our strategy was as obvious as it seems. Forget about original speakers, don’t let a replaced tranny run you off (we’ve never replaced one with a Mercury that didn’t sound better than the original), and deliberately track down the fuglies told girls you can find from the tweed era. Busted baffle boards? We luv that….Ricky-ticky cabinets are good, and the coverin’ don’t matter. What you want is a beater with a totally neglected chassis and as many of the original fat Astron caps and original resist or present as possible. Yeah, some of them may have to be replaced, but it’s far better to allow a prudent and judicious amp tech determine that rather than buying an old amp that has been raped by a hard chargin’ cowboy hooked on Sprague Orange Drops.Buy one of those and your old amp will sound new,never to sound old again, and that’s most definitely not the play you want to make here. A little component drift is good.
There is luck involved, too… not all vintage amps were created equal. Some of them left the birthing bench endowed with incredible tone – a happy accident created by the melding of variable components that resulted in extraordinary sounds. Others were created by the same roll of the dice, but with a different outcome altogether – mysteriously dull, flat, or simply lacking whatever you wish to call it… that tone, mojo, bloom, the harmonic complexity of your first Schlitz, depth, fatness… whatever. To experience the blissful afterglow of unanticipated discovery, you must be willing to risk something, which is another way of saying that faith must be exercised in the absence of a guarantee. In this respect, buying old amps is a lot like life itself…. The greatest obstacle to discovery is the flawed perception of an impossible challenge. And the window of opportunity is closing on these great old amplifiers faster than you may think. Like vintage guitars, the best old amps are being taken out of circulation by col-lectors willing to pay prices that are based on potential future value (more than they are worth today, perhaps, but less than they will be worth tomorrow). For you, hombre, the time to bust a move is now.

We always maintain a steady flow of gear arriving for review, but sometimes we also employ a fascinating if time-consuming research strategy that involves logging onto eBay, picking a broad category such as “guitar amplifiers,” and settling in for as long as it takes to patiently scroll through every page of listings. Yeah, that’s often 50 pages or more, but since we can’t possibly think of all the items that might interest us and search for them by name, it’s far more revealing and productive to just hunker down and scroll. Rarely do we fail to find something intriguing that would have otherwise been missed, and such was the case on a morning in August when we stumbled on a listing for a 1959 tweed Deluxe. Were we looking for a tweed Deluxe? Nope. Wouldn’t have crossed our mind at the time…. We had already reviewed 5E3 reproductions from Fender, Clark and Louis Electric within the past 3 years, and we have frequently referenced our 1958 Tremolux as being our desert island #1. Isn’t a Tremolux just a tweed Deluxe with tremolo in a bigger box? No… not even close. That would be like saying you wanted to date a blonde – any blonde. For the record, our fixed bias Tremolux possesses a cleaner tone with a bigger, booming voice created by the taller Pro cabinet. The Two Fifty Nine is a completely different animal….
Sporting a February 1959 date code on the tube chart, the ’59 had been listed by a seller in Arkansas who turned out to be Tut Campbell, formerly a well-known guitar dealer in Atlanta. Still buying and selling gear, Campbell had described the Deluxe as being in original condition with the exception of a replace output transformer – a big old mono block Stancor dating to 1957. Given the otherwise original condition of the Deluxe, which included the Jensen P12R, we made Campbell a “best off” below his asking price and scored the amp for $1,850 shipped. We wouldn’t say we stole the Deluxe, but it seemed a fair price of admission for the opportunity to experience and explore still another rare classic and supremely worthy piece of Fender history on your behalf.
The Deluxe arrived with the big Stancor dangling from the chassis despite Campbell’s careful packaging. Wasn’t his fault, really – in a feeble effort to avoid any additional holes being drilled in the chassis, the fellow who installed the Stancor in the ’60s had merely tightened set screws over the small tabs at the base of the heavy tranny, which was designed to be mounted upright – not hanging upside down in a guitar amplifier. Of more concern was the fact that while the amp was lighting up, there was no sound…. Well, we’ve been here before, so we made a call to God’s Country and the Columbus, Indiana domicile of Terry Dobbs – Mr. Valco to you. We had already set aside a spare output transformer (Lenco, McHenry, IL) that had been the original replacement installed in our ’58 Tremolux when we first received it, replaced with a Mercury Magneticsfor our June ’07 review article. Mr. Valco cheerfully answered his phone and as we explained the situation with the Deluxe he agreed to walk us through the installation of the new replacement – a simple process involving four lead wires being connected to the rectifier and output tube sockets, and the speaker jack. As long as you put the correct wires in the right place, a piece of cake, and we had the new tranny in within 10 minutes. Pilot lamp and all tubes glowing, still no sound…. Valco patiently guided us through a series of diagnostics with the multi-meter and the Deluxe was running on all cylinders, pumping 380 volts. Stumped, and with the hour growing late, we called it a day. Leaving the mysteriously neutered Deluxe chassis on the bench until tomorrow.
Morning came with a whining voice delivering a plaintive wake up call – “It’s got to be something stupid and simple….” Inspired by a huge steaming mug of Jamaican High Mountain meth, we sat back down at the bench, tilted the innards of the Deluxe chassis forward beneath a bright halogen desk lamp and peered in for answers. We began slowly examining the chassis in sections, looking for broken or dull solder joints, loose or broken wires, while gently pushing and prodding wires and connections with the eraser tip of a #2 pencil as we had seen Jeff Bakos do so often at his bench. After ten minutes or so we were about to give up, when we turned our attention to several places where the circuit was grounded to the chassis adjacent to the volume and tone pots, and damned if a solder joint for one of the uninsulated ground wires hadn’t separated from the chassis. No ground, no sound, and as soon as we had restored the solder joint the Two Fifty Nine arose from the dead with a mighty A major roar.
The amp was indeed remarkably well-preserved in all respects, with the typical amber patina of old tweed. The burnished chrome control panel remained bright and clean with no corrosion, the original handle remained intact, and a couple of small ciggie burns on the edge of the cabinet added a stamp of historic legitimacy to the Deluxe’s pedigree. The top half of the Jensen’s frame was coated in a fine film of red clay dust from the Delta, and while the cone was in remarkably good shape with no tears, an audible voice coil rub called for a recone. We would send the speaker to Tom Colvin’s Speaker Workshop in Ft. Wayne, Indiana, requesting that he leave the original unbroken solder joints for the speaker wires intact if possible.
Meanwhile the first order of business was to listen to an assortment of NOS tubes from our stash, and audition no less than a half dozen speakers. Different sets of power tubes and individual preamp tubes will sound surprisingly different, so we started out with a matched pair of NOS RCA 6V6s, a GE 5Y3 rectifier, and an RCA 12AX7 and 12AY7. From there we subbed in a dozen different RCA, Amperex, Tesla and GE 12AX7s, noting varying levels of brightness, warmth and intensity among them all. For an edgier, more aggressive voice, the GEs and Amperex typically deliver the goods, while RCAs produce a slightly warmer, richer, fuller tone. We also experimented with a 12AT7 and 12AX7 in place of the lower gain 12AY7, and while those tubes ramp up gain and distortion faster and with more intensity than the 12AY7, they seemed like overkill for us. Our Deluxe possesses a tone of gain using the stock 12AY7.
Rather than repeatedly reloading the Deluxe with different speakers, we used a Bob Burt 1×12 cabinet built from 100-year-old pine for our speaker tests. The original Jensen had never been pulled from our amp, but multiple speaker replacements in an old Fender inevitably cause the speaker mounting screws to loosen in the baffleboard, making speaker swaps unnecessarily clumsy and complicated. When we do run into loose mounting screws, we simply run a few small drops of Super Glue around the base of the screw and surrounding wood. Allow to dry and your screws will stay put provided that you don’t torque the nuts on the mounting screws like an idiot with a socket wrench. Don’t be that guy,
We tested a range of speakers that included a Celestion G12H 70thAnniversary, Colvin-reconed ’64 Jensen C12N, Eminence Wizard, Private Jack, Alnico Red Fang, Teas Heat, Screaming Eagle, Red, White & Blues, and Warehouse Green Beret, Veteran 30, Alnico Blackhawk and Alnico Black & Blue. The Alnico speakers generally produce a tighter, smoother, slightly more compressed tone, with a variable emphasis on upper mid-range and treble frequencies, while the speakers with ceramic magnets possess a wider, more open sound. Higher power ratings of 75W-100W offered by the Red, White & Blues, Screaming Eagle and Warehouse Blackhawk typically translate into more graceful handling of bass frequencies, and in a 20 watt Deluxe, zero speaker distortion, for a clean, powerful voice.
Let’s cut to the chase with speaker evaluations, shall we? It has become clear to us that even after reviewing a dozen speakers in as much detail as mere words allow in a single article, many of you remain uncertain about which speaker to choose. No kidding. We would absolutely love to hand you a single magic bullet when it comes to speaker swaps, but here’s the dirty little secret about choosing speakers…. The overall character of the amp you will be installing your new speaker in is critical, and to some extent, the type of guitars and pickups you play most often are important, too. Tailoring your sound with the unique gear you play is not a one-size fits-all proposition – you have to invest some thought into the process. Are you going for a classic “scooped” American Fendery tone, or something more British, with a bit of an aggressive edge and upper midrange voice? Are you playing guitars with single coil pickups or humbuckers? Is there a specific, signature tone you are searching for, or are you playing a wide variety of musical styles that requires a broader range of tones? Do you like the more open sound of speakers with ceramic magnets, or the smoother compression of Alnico? What are you not hearing from your amp and the speaker that’s in it now? Do you want a brighter tone, darker, better bass response, or fuller, more prominent mids? Do you want to really drive the speaker and hear it contributing to the overdriven sound of your amp, or do you want a big, clean tone with no speaker distortion in the mix? The truth is, if you don’t know what you want, you are far less likely to get it. On the other hand, nothing is accomplished with paralysis by analysis. To be perfectly honest, there are lots of speakers made by Celestion, Eminence, Warehouse and, if you can wait long enough for them to break in, Jensen, that we could and would be perfectly happy with, but we would also choose them carefully, taking into account all the factors mentioned above. After a couple of days spent swapping speakers, we ultimately concluded that we preferred the ’64 C12N for a classic tweed Deluxe tone, and a broken-in Celestion G12H 70th Anniversary for the most mind-altering 18 watt Marshall tone we have ever heard. Seriously. More on that in a minute….
Having split more than a few hairs with our speaker swaps, it was time to start picking nits off of gnats with some output transformer evaluations. We first contacted Dave Allen of Allen Amplification, who also stocks Heyboer transformers built to his specs. We found a variety of appropriate output transformers on Allen’s site that offered subtle variations on a stock original Deluxe OT, and we asked Dave to describe the TO26 model we wished to try in the Deluxe:
“The TO26 was intended as a hot rodding upgrade to a stock Deluxe Reverb OT. While maintaining the stock 3-1/8” mounting centers, its fat stack of hotter core steel and multi-tap secondary make it a good choice for builders wanting to maximize the performance of a pair of 6V6s and who may also want to push the envelope with 6L6/5881s while still being able to clear the speaker in a stock cabinet. There are physical limitations in small amps, so its short low profile is welcome. The orientation of the laminations is also good for low hum pick up from the power transformer. I found that an OT mounted the tall way (like my TO30D) picks up considerably more hum simply due to its orientation to the power transformer, so, shoe-horning a ‘tallish’ OT into your amp may cause it to pick up hum from the power transformer – not much of an upgrade. “The TO26’s 7K to 8 or 16 ohm rating makes it ideal for a pair of 6V6s as well as 3,500 ohm to 4 or 8 rating for 6L6/5881s. Notice you always have an 8 ohm option with both types of power tubes. An impedance switch could be wired (I use a blackface grounding switch) as a power tube type selector for an 8 ohm speaker to go between 6V6s and 6L6s. The TO26 will typically give slightly more output with 6V6s due to its more efficient low-loss core steel and will keep the bass clean longer for more perceived clean headroom. As it takes the most watts to reproduce the bass, you notice distortion there first, and since Fender-type amps are so bass heavy, you can quickly hit the wall with headroom, so a noticeable increase in clean bass response certainly feels like a more powerful amp with the TO26. It is kind of like you installed a new speaker with a larger ceramic magnet that is more efficient than the old speaker. The amp is a little louder and the bass a little tighter or cleaner.
“There seem to be a lot of 6L6-based 5E3 amps out there now to get a little clean headroom from a circuit normally not known for much of that. The TO26 is a good choice for that type of amp as it will fit typical available chassis and cabinets. It has extra long 12” topcoat leads ready to strip and solder. I would reckon it would handle up to about 30 watts before starting to saturate and compress – plenty of cathode-biased 6L6s. I find that the Heyboer paper stick-wound and interleaved output transformers with premium core steel and heavy core stacks have typically better clarity or definition than ‘stock’ OTs. Call it fidelity or whatever you want – just clearer distorted and complex tones and better separation of notes in chords, etc. I use the TO26 in the Allen Sweet Spot, Accomplice Jr. and Hot Fudge with Nuts amps with excellent results. All of these amps can use either 6V6 or 6L6 power tubes. You know how a 5F6-A or Super Reverb has that huge 4 bolt OT for a pair of 6L6s to get the maximum clean bottom end? That is sort of what the TO26’s OT is to a pair of 6V6s. It just doesn’t even come close to saturating.
When we informed Dave that we planned to run the Deluxe with 6L6/5881 power tubes as well as 6V6s, he recommended that we try the TO26 since it had been specifically designed for such applications. He also sent a smaller TO20 transformer, described as being designed with a wider 1-1/4′′ lamination “fat stack” that provides 60% additional core mass than typical ¾′′ stack units for improved performance. The TO20 is a direct replacement for Blues Jr. and Princeton Reverb amps, and also suitable for dual EL-84 amps with an 8 ohm load.
Mr. Valco also sent us a replacement 5E3 output transformer he had bought on sale from Clark Amplification a few years ago made for Mike Clark by Magnetics Components in Schiller Park, IL – a company that has been producing transformers since 1943, having been the primary supplier for Valco and various Gibson amps in the ’50s and ’60s. A call to the company revealed that ToneQuest ReportV12. N1. Nov. 20104the transformer Valco sent was essentially their replacement for a Deluxe Reverb, model #40-18002 without bell ends per Clark’s request. We also learned that the company offers a complete range of Classic Tone vintage power and output transformers, including a reverse-engineered clone of a ’55 Triad 5E3 output tranny, model #18022.
We also contacted Paul Patronete at Mercury and requested a ToneClone “brown Deluxe” output transformer, since Larry Cragg had provided them with specific measurements from original OT in Neil’s ’61 tweed Deluxe, confirming that it was indeed a ’61–’62 brown Deluxe tranny. With a total of 6 output transformers to listen to, we took the Deluxe to Jeff Bakos, who set up a rig on his bench that enabled us to clip in each transformer and very quickly switch back and forth between them as we played a guitar through the amp. Are we having fun yet? Here’s what we heard:
Lenco – An excellent authentic “vintage” vibe for those that prefer the classic, if somewhat murkier sound of a tweed amp being pushed, lots of sag in the low end and a jangly pop in the top. And “old,” rather “lo-fi” sound indicative of the ’50s era amps.
Magnetics Components Clark Deluxe 18002 – Similar to the Lenco, but stronger and more robust, with a prominent growling character and voice. Thick, wooly and willin’ with better treble presence and clear string definition then the Lenco, yet an entirely “vintage” character. This tranny is comparable to those found in Deluxe amps from the brown era through silverface. Excellent power, punchy and fat with exceptional clarity and tone.
Magnetic Components 5E3 Clone – Percussive and dynamic with a faster attack response than the Clark/Deluxe Reverb version, this transformer was reverse-engineered from an original ’55 Deluxe OT. IT imparts an intense, throaty tweed character with enhanced mid and treble presence, remarkable clarity, and an authentic vintage ’50s vocal tone with softer bass response and slightly less volume and power than the Deluxe 18002.
Allen/Heyboer TO20 – An interesting variation with a much more modern, percussive dynamic character. The sound was not as heavy and imposing in the vintage style, and with this transformer the Deluxe reminded us of the more refined sound of a Fender Princeton, with excellent dynamic punch for slide and Allen/Heyboer TO26 – As advertised, the low end held up loud and proud with very little sag and an audibly higher threshold of clean headroom, although beyond 6 on the volume control the Deluxe was still holding nothing back. Overall, this transformer imparts a cleaner, high fidelity tone with more clarity and stout bass response than a typical stock 5E3 transformer. An excellent choice for enhanced low-end and maximum volume.
Mercury Magnetics brown Deluxe – Immediately recognizable, the Mercury displayed a trademark sound that is smooth, exceptionally musical, warm and balanced. Sounding more “high fidelity” than the Lemco or Magnetic Components transformers, but still seductively unruly enough to get yer ya-ya’s out. Sweet, rich, detailed and sticky.
Now, you may be wondering why we would bother to audition so many output transformers…. How much difference can it make? Well, forty-odd years ago when someone rigged that old Stancor tranny in the Deluxe, the only choice available to most repair shops was whatever was on hand in the scrap pile. Today we can shape the tone and dynamic response of an amp with a variety of “vintage” or more modern, custom transformers that allow us to recapture the original sound and feel of the amp, or improve upon the original design. Why did Cesar Diaz install output transformers for a Twin Reverb in Stevie’s Super Reverb amps, and Bassman transformers in his Vibroverbs? Because the first thing that chokes and overwhelms a smaller output transformer are the bass frequencies, and Cesar wanted Stevie’s amps to produce a rock-solid, thundering low end that could handle his massive wound strings. The tone we’re celebrating with our ’59 Deluxe is quite the opposite…. The raucous sound of the amp teetering on the edge is the key to it’s exploding tone, but if you wanted to go in the opposite direction with more headroom and a tighter low end, transformers like the TO26 have been specifically designed for that purpose. We once replaced the output transformer in our Pro reverb with a bigger MercuryToneClone Bassman, and the Pro grained a tone of clean headroom and unyielding bottom. Wanna make it even harder still? Use a plug-in diode rectifier in place of the 5AR4 rectifier tube. No saggy britches now. As with so many choices we make in the Quest for tone, the final decision comes down to your mission and individual taste, and Jeff agreed that between the Heyboer TO26, both Magnetic Components trannies and the Mercury brown Deluxe, the question wasn’t which one was “best” – all four were exceptional, but different. Some players would prefer one over another for different reasons described here, but all of them represent stellar examples of just how far we’ve come since the day that old Stancor tranny was used to put the Two Fifty Nine back into service.
One last detail needed to be addressed…. Could we safely run the Deluxe with 5881s or 6L6s if we preferred that sound over 6V6s? Once again, we asked the prescient Mr. Valco for some Hoosier insight:
“The impedance mismatch in this particular amp using the 6L6s is really not a big concern, it won’t hurt the amp and will either sound good or it won’t. The 6L6s draw 1.8 amps and two 6V6s draw 0.9 amp, so using the 6L6s will add about 1 amp more current draw that the power transformer needs to supply from the 6.3 volt heater windings. On some small 6V6 amps, using 6L6s can and does cause the power transformer to run hotter because more current equates to more heat. The concern is that the power transformer in the Deluxe, not being a large one to start with, has the extra 1 amp of heater current capacity to safely use the 6L6s. One way to determine if the power transformer is really stressed out with the 6L6s is to measure the AC heater voltage on pins 2 and 7 on the power tube sockets (or on the pilot lamp) and see if the AC voltage drops significantly from the reading using 6V6s versus 6L6s. It should be a bit over 6.3 volts AC with the 6V6 anyway (since the wall voltage is higher these days than in the early ’60s) and with the 6L6s you sure don’t want to see a large drop in voltage below 6.3 volts AC. If there is a large drop it means the transformer is having trouble supplying enough current for the 6L6 heaters if given enough time with the 6L6s could damage the power transformer. If the drop is only a few 10th of a volt, and doesn’t go below 6.3 AC, then it would indicate that the transformer is supplying the demand for the heater current and should be OK. Most Fender amps used power transformers that could handle some extra current demand.
And now we arrive at the moment of truth. We’ve been steadily reeling in a parade of new and classic amps for review in these pages for 12 years now this month – Marshall, Fender, Magnatone, Hiwatt, Vox, Valco, Silvertone, Ampeg, Gibson, Gretsch, Mesa Boogie, Park, Supro, Dickerson, Traynor, Budda, Western Auto, Standel, Dumble, Cornell, Clark, Crate, Divided by 132, Reeves, Bad Cat, Gabriel, Fuchs, Koch, Star, Category 5, 65 Amps, Balls, Bakos, Callaham, Blankenship, Reinhardt, Grammatico, Siegmund, Chicago Blues Box, Roccaforte, Headstrong, Rivera, Mad Professor, Talos, Maven Peal, Reverend, BC Audio, Savage, Goodsell, Fargen, Carol-Ann, DST, Two Rock, Germino, Matchless, Louis Electric, Swart, Demeter, Juke, Aiken, Bluetron, DeArmond, Carr, Victoria, and Dr. Z, with more coming. Lots of amplifiers, multiple models from the same builders, and among the foremost classics – Fender, Marshall, Vox, Hiwatt, Gibson, Ampeg and the entire Valco catalog, we have acquired, optimized and restored dozens of amps considered to be among the most desirable vintage models ever built. In the 20 watt wheelhouse occupied by the Two Fifty Nine, it has no equal by a mile. Game over.
After a lot of back and forth testing with different sets of output tubes, we became hooked on the thundering sound produced by a pair of Philips small-bottle 6L6WGBs. Thanks to Larry Pogreba’s talent for scavenging rare tubes (in Montana, no less), we are flush with several outstanding and stout pairs of RCA 6L6s, but the brighter Philips really lit up the Deluxe with a fresh and lively attitude that mirrors the bounce of a newer amp. With the ’64 Jensen C12N loaded, the Deluxe spookily nails the tones of Neil Young’s rig on Ragged Glory – a “studio” recording cut live with the Deluxe and Old Black in a barn on Young’s ranch with Crazy Horse. With the volume backed off to 4-5 a bluesy jangle emerges anchored by solid low end, rich midrange, the sweetest treble tones imaginable, and variable levels of sustain and edgy distortion that can be controlled both by the volume on the guitar and pick attack. The Deluxe does not discriminate between single coils or humbuckers, ravaging both with equal fervor, and the responsive dynamic character of this amp simply is not of this world. Rotating the single tone control sharpens treble without dumping lows or mids, while also subtlety increasing gain, as if you were using a boost pedal. A “Y” cord plugged into the Instrument and Microphone inputs enables the two channels to be mixed with great effect. As Neil Young described, bringing the mic input volume up with the instrument volume set between 6-8 gradually deepens the tone while slowly igniting an intense explosion of thicker second order harmonics and distortion as the dynamic character of the amp softens. Pushing the Instrument volume level up into the 8-12 range brings the volume up to a perceived level that exceeds 20 watts, while provoking an angry, pissed-off cascade of astonishingly rich musical distortion as the notes swerve into controlled harmonic feedback.
Switching from the Jensen to the Celestion transforms the Deluxe into the most stunningly toneful 20 watt Marshall you could possibly imagine. To be honest, you probably can’t imagine it, because we have never heard anything like this ourselves, even after owning a couple of vintage Marshall PA20s, a rare Lead & Bass head and 1×12 cabinet, and a Balls 2×12 18 watt. We could easily live with either speaker, and the Deluxe also just kills pushing our 8 ohm 4×12 pinstripe cabinet.
For those of you who appreciate a somewhat tamer vibe, we can assure you that the Deluxe loaded with a fine pair of 6V6s is equally mind-altering. The overall sound is a wee bit smaller in girth and less imposing, yet abundantly overflowing with vivid harmonic depth, a supremely touch-sensitive response, and brilliant combination of fidelity, clarity and bloom. Compared to a black or silverface Deluxe Reverb, the ’59 presents a more musically complex soundstage, less harsh, stiff and linear, and it lacks both the sharper treble of a blackface amp, and the scooped midrange character. The tone is rounder and meatier, the treble sweeter and less dominant, with an enhanced 3-D image.
Now, if you’re the type that skeptically requires a qualifier to add a stamp of legitimacy to such an over-the-top review, here it is, Mr. Been There-Done That…. The Deluxe doesn’t and won’t spew big clean tones at stage volume. Our ’58 Tremolux produces a cleaner tone with a higher threshold of clean headroom by far at comparable volume levels, and the taller tweed cabinet encourages a stronger, cleaner resonant bass and low mid response. The Tremolux is also equipped with a Mercury ToneClone Tremolux output transformer, which creates a tone that is less wooly, raucous and indistinct.
The busted-up sound of the Tremolux above 5–6 is gloriously righteous indeed, but with more clarity and less provocative intensity than the Deluxe. Taken in context, what we’re suggesting here is that in our experience, the Deluxe has no equal as both a Fender and Marshall style 20 watt rocker (depending on speaker selection), and we’ll add “blues” to that description equipped with 6V6s and the Jensen C12N. During our 2-month test period, we also routinely used our Lee Jackson Mr. Springgy reverb, Analogman-modded Boss DD3 digital delay, and a very cool, versatile (and cheap) Flip tube tremolo pedal reviewed here. Can a modern replica of the 5E3 Deluxe deliver the same inspiring tones as the Two Fifty Nine? The closest thing we’ve heard is the Louis Electric “Buster,” but no, magical happy accidents like this Deluxe can’t be reproduced today – and that is as it should and shall always be. Quest forth…

In this issue we are dealing with a subject on which I have received many inquiries in the past. It is about the selection or matching of tube amps for the best possible Jazz sound. Amplifying acoustic or semi-hollow-body guitars has always been a huge challenge because most jazz guitarists are very demanding in terms of sound and simultaneously fight against unwanted distortion and feedback. In the following article I would like to summarize some tips and tricks that get great tone and how to avoid distortion.
When I started getting involved with jazz sounds, around 1977, most guitarists in this genre used transistor amplifiers. George Benson played a Polytone, Pat Metheny an acoustic amp with a 4×10” speaker cab and Volker Kriegel and Michael Sagmeister used a Gibson LAB L9 with 15” speakers. Such examples can be found very often from that period. Although all of these guitarists had indeed very good tone, the typical depth and openness of a tube amp sound could not be reached however in its wider spectrum. Still the transistor amps had some advantages over tube amps: They sounded very compact and linear, were less prone to feedback and offered a relatively balanced frequency spectrum and a nice sustain, which was the ideal sound of many jazz guitarists. A Gibson L5 played through a LAB or a Polytone is completely convincing – even today.
One disadvantage that the transistor amps had in particularly was its dynamic behaviour, in their relatively poor response and in their tendency to not let the individual character of a particular guitar fully unfold. You could also say: Transistor amps tend to standardise tone.
I do not wish to start a discussion about tube versus transistor because transistor amplifiers will continue to play a rightful role in jazz. It is more about ways to show how one can get the typical warm jazz tone with a tube amp without all the disadvantages.
Above all I am thinking of the sounds of the early sixties, which were marked by numerous jazz guitarists including: Wes Montgomery, Kenny Burrell, the early George Benson, Herb Ellis, Joe Pass, Barney Kessel, Grant Green and Jim Hall. All of these guitarists were playing tube amps on their early recordings and getting fantastic sounds. Today tube amps are celebrating a renaissance with jazz guitarists.
Let us first take look at the most popular models from the distant past. In the fifties the combos from Fender (Tweed), Gibson, Standel or Flot-A-Tone were especially loved by jazz musicians due to their sound and their small size. These amplifiers were sufficient for jazz guitarists because they were usually accompanying musicians and they performed as a soloist only in rare cases. They often stayed in the background and did not play very loud.
Even back then, most jazz guitars were equipped with a tone control that made it possible to filter out unwanted peaks and thus to form the typical dark jazz sound. But soon the guitar became a solo instrument. Just think of the impressive sound of a cascading Les Paul, who at that time had good reason to play on a solid body. The traditional jazz players remained with their hollow bodies and now had to fight against all the disadvantages of the electrification of their sounds. Recently I read in a retrospective of Wes Montgomery that he alleged that during his entire career he was unhappy with his sound because he simply could not find the perfect amp. One might even go so far and assume that the dark jazz sound is actually created only (and eventually cultivated) because the amount of unpleasant highs tube amplifiers have, are rather imperfect sounding and also quickly led to feedback. Most guitarists wanted more of a linear and natural reproduction of their beautiful instruments that already sounded great acoustically.
Let’s now take a look in the interior of a tube amp and consider certain circuit characteristics which can be modified for a better jazz tone. The objectives of these measures are the reduction of distortion and the high frequencies, improving the mid-range and increasing the linearity of the sound.
First, a list of known suitable amplifiers for conversion to a “jazz box”: Fender Tweed Fender amps from 1956 and Brownface, Blackface and Silverface combos. Examples from this list shall be explored in following issues.
Let’s start with a Tweed Deluxe amp replica from Cream which I have converted for jazz sounds. These amps are known for their distortion when left stock and therefore not ideal for a clear jazz tone. But they are very small and handy and with around 15 watts of power ideal for use in a club. In addition, these amplifiers are connected with a so-called “split-load” phase inverter which is appropriate for our purposes because of its low gain. The only drawback is the two coupled volume pots, which restrict the volume control range on the one hand and deliver too much gain in the preamp. The aim is to reduce the gain in the preamp and increase the output power and stability of the amplifier. Only then we get enough headroom for a clear sound.
Just this once, I should like to “put the cart before the horse” because there are a number of measures to improve the amp without intervention on the circuit.
First, these amplifiers usually have an inefficient speaker. Powerful speakers with a good efficiency rating are especially suitable for jazz sounds. Those who love the Alnico sound can search out an old JBL D-120 and replace the aluminum dust cap with a counterpart out of fabric (available from Weber VST). The speaker can be helped dramatically in the highs and we get a warmer, rounder tone. Excellent was also the old Fane Crescendo Heavy-duty speaker, which is also suitable after the removal of the aluminum dome making a perfectly clear and powerful sound. These speakers were also used by David Gilmour. Another excellent choice is also an Electro-Voice 12L or a Jensen C12K with 100 watts. All these speakers better the sound of the Tweed Deluxe significantly. You only have to watch out for the thin baffle-board because vibration during transport could for example pull heavy speakers from the screw holes.
A further stabilizing method is the conversion of the power tubes to 6L6 or 5881, which I recommended at this point several times. Although the amp has only about one or two watts more output, the increase in headroom is very clear. You get more clean reserves and dynamics. Here I recommend changing the cathode resistor of the amplifier from 250 (typically with 5 watts) to 330 ohms with 10 watts. If you play a jazz guitar with humbuckers, we recommend the low input of the normal channels. Here there are less highs and the output signal of the guitar is more attenuated. It should be noted that the volume pots affect each other on the Tweed Deluxe. By turning the unused channel by not more than 70 percent, the tone is much cleaner, but also quieter.
If you don’t wish to utilize this trick, you can simply remove the cathode of the second stage capacitor (Elko 25mF/25 volts) and reduce the gain of this stage substantially, which in turn increases headroom. The amp will be clearer and somewhat linear, but also a touch softer.
Even more clear sound can be obtained by replacing the output transformer. Something I always do in such tuning. In this case I choose a Mercury Magnetics Tweed Pro Axiom FTPRO-O transformer (available at Tonehenge Amplification) with 8 ohms, which gives much more stability to a small tweed amp.
If you want to use the amp only for jazz, you can also decouple the two volume controls from each other and only one channel and a tone control remain. Now you can adjust the volume much finer and linear. The circuit can be found at www.schematicheaven.com under Fender Deluxe 6G3. Here the channels are completely separate, each with their own volume and tone control. It’s only after the volume knobs on the channels that two 220k ohm mixing resistors are mixed together again.
Since the Tweed Deluxe played with humbuckers has in general somewhat bassy sounds, I also reduce the value of the coupling capacitors from 0.1mF to 0022mF. This makes the sound tighter and more mids. Sprague “Orange Drop” P715-type fit perfectly here.
Finally we get to fine-tuning via preamp tube placement. With a good 12AY7 and a 12AX7 of your choice, you can continue to shape your favourite tone. For those of you who have not had enough, you can play with the value of the capacitor on the tone-pot. The Deluxe was originally installed with a 0005 UF capacitor but also possible are values such as 0.01mF or 0.02mF (as in the 6G3) for a slightly warmer tone. If you want to darken the sound one can bridge one of the anode resistors at the 12AY7 with a 0.003mF capacitor (as in the normal channel of the Brown Vibrolux).
The result is a truly compelling jazz amp for small clubs, feeds back less, offers more clean reserves and could compete with any Polytone but all the benefits of dynamic and harmonically rich tube sound can be enjoyed. Diana Krall’s guitarist Anthony Wilson often used a Tweed Deluxe replica from Clark and his blond Gibson Byrdland in the studio. This sound is very reminiscent of Kenny Burrell and offers a wonderfully unique character. Have fun experimenting!

Like the pedal business, the number of amplifiers being built by smaller builders has mushroomed into a garage and basement Skunkworks industry that is constantly changing. New guys pop to the surface and ride the momentum created by chat rooms and social media, while others quietly slip beneath the surface in an unfortunate imitation of Beach Boys drummer Dennis Wilson, never to be heard from again. The desire amongst certain guitarists and collectors to own the latest, supposedly greatest new amplifier is a power drug, and for some, a hard habit to kick. We enjoy discovering small batch alternatives to familiar archetypes and affordable production amps, too, but since we’re doing so on your behalf, our initial evaluation process lacks the unbridled enthusiasm of a new owner who has already made the plunge financially and emotionally. Still, when a giddy reader calls or writes asking us to review their new killer amp, we routinely hit the builder’s website, send an introductory email and wait for a response. Such was the case with the Tungsten Cremawheat and builder Adam Palow
Ultimately, the Cremawheat turned out to be another exceptional amplifier as our review reflects, but as is so often the case, the story behind the name on the face plate is as interesting as the amp. Listen….
TQR: You mention on your website that you were inspired and intrigued many years ago by your first tube amp. Do you recall what it was?
It was a 1965 Fender Vibro-Champ that was missing the face plate, and the grill cloth had been replaced with a red and black check material that looked like it had been on a sofa. I think I was around 16 when I got it, and no matter what I played through it, the amp sounded very musical compared to the solid state practice amps had used before. It was the beginning of an obsession. I started chasing down vintage Fender amps wherever I could, and I met a guy who showed me how to safely drain the stored voltage in an amp, how to use a soldering iron, and he explained how bigger caps produced more low end. From that point forward I was on my own, and everything I have done since has been the result of trail and error and experimentation. I’m limited in some areas because I don’t necessarily understand all the theory, but in another sense it’s empowering because I am chasing feel and working in an intuitive way rather than strictly by the “book.” My favorite part of the build is constructing the board and wiring the chassis. If there is any artistic expression in building an amplifier it’s in the way the board is constructed. Of course, in the larger picture, it’s completely meaningless.
TQR: What were the most significant things you learned through hands-on experience working with guitar amps, and the five years you spent working on Hammond organs with Bob Schleicher?
The thing that blew my mind the most once I had acquired multiple identical models of the same amplifier like the Fender Blackface Bassman and Bandmaster was how different they could sound from each other even though they were built with the same components. That also carried over into my work with Hammond organs, because every large Hammond console also had its individual voice, and I attribute that to the accepted variance in parts values, and individual and very unpredictable drift in these values over time. You also see random parts stacking where some of the capacitors may have been oriented the correct way and others not. When all the caps are pointing the right way you can have an amp that sounds faster, and when they are oriented the wrong way the amp can sound slower. On the old caps there was usually a band marking the outer foil, and whether or not they were oriented correctly often just seems like chance. Some companies paid strict attention to that and others did not. Even if I am building ten identical amplifiers in my own line, there are going to be variances between them – not only in the tolerance stacking, but in the way the tubes bias to the cathode resistor. I have an absolute minimum standard – it has to inspire me or I’m not going to ship it out, but every once in a while you drop in the right rectifier and the right power tubes and they just match up perfectly with the cathode resistor and it makes your hair stand up on end. Magical. Yet that same amplifier with a different set of tubes may not do the same thing.The Hammond organs are unique because not only do they have an extremely rich and harmonically complex signal, but they have infinite sustain with no transient attack unless you’re using the percussion feature, so when you’re dealing with Leslie power amplifiers you’re not dealing with sag. You’ve got compression going on because you’re driving it with a very wide band signal, but because there is no transient, you’re not experiencing sag, compression and release in that order. I spent a lot of time rebuilding Leslie amplifiers, and there was a very specific type of distortion coming from those 6550 Tung-Sols – a low, grinding, wooly distortion kind of like the Marshall of the organ world in a lot of ways, and I caught that sound in my head. It was very musical, and it had a lot of clean qualities, but also an outrageous amount of overdrive on tap, and even when it was driving hard there was still enough clarity to retain a musical quality in the distortion. You could really hear the notes and the intervals between them, and that’s the complaint I had with a lot of amplifiers outside the vintage world…. They swung so far into breakup and distortion that you lost the clarity of the notes. There was more noise than tone, and the place I’m coming from is a more musical place. The other aspect of my work with Hammonds is that I gained a huge amount of experience with vintage Jensen Alnico speakers.
TQR: We have always wondered if the Jensen speakers used in Hammond cabinets were similar to those made for guitar.
In the Leslie, the Alnico P15LL and later C15NLL bass driver that shoots down into the rotating horn were definitely not guitar speakers by any stretch. The 12 inch Jensens I’ve seen bear all the same markings as standard Jensens for guitar, the differences being that they have black frames with no Jensen sticker, and the Hammond code starting with the letters “AO” have been silk-screened on the frame. I have pulled P12Ns out of old Hammond A100s, as well as P12Qs, and if they were specifically designed for organ, they are also the best sounding guitar speakers I have ever heard, and I have used them to base my own speakers on made by Weber.
TQR: Which prompted the development of your own line of proprietary speakers?
Yes, and I didn’t really have to start from the ground up because they had already come close to the mark, but I wasn’t hearing the same extended frequency response that I was hearing from the vintage speakers, and it was just a matter of developing a different recipe. Fortunately, when Ted was still alive we went through the process of mixing and matching components, just trying to get that sound. I didn’t care if the parts were period-correct – I just wanted them to sound right. I tried to do the same thing with the ceramic line, but we just never nailed it and I never put them into production. Of course, the goal in developing the Alnico speakers was to produce the low-wattage, medium fidelity, $6 replacement speakers that they were originally.
TQR: Looking at the different models you build today, it’s obvious you prefer the sound of tweed-era amplifiers.
Yes, I cut my teeth on blackface amps, but when I built my first tweed Champ I became one of those guys that ditched my pedalboard and plugged straight in. For me it’s all about that very alive midrange, and the dynamic response you get out of the power section. I was instantly hooked. I also have a fondness for the lower power brown amps as well, but when it comes to what I personally want to plug in to and play, I really need to feel the response of a tweed power section.
TQR: What’s your approach to specific types of capacitors used in building your amps?
You have to let your ears be the guide, and everyone hears things differently. Every quality capacitor has its place, but I personally prefer the sound of Mallory 150s in tweed amps. Other people feel that they are too bright in the upper mids until they break in. I tend to break in my amplifiers for 72 hours and when I take breaks from building I’ll plug into every amp that’s burning in. The truth is, everything matters. In the Cremawheat, for example, there different capacitors are used in the tone circuit to color the tone in a certain way. It’s one recipe. I also use custom-wound Mercury Magnetics transformers in everything. Some of them are custom-wound because I wanted a different gauge of wire, and others because I wanted a different secondary voltage. When we’re talking about power transformers, voltage that you’re sending out to the circuit makes much more difference than the brand you’re using. With output transformers it becomes more critical. Some people want to hear a darker transformer, others high-end clarity…. Some people want a smaller core so it saturates sooner, and others want enough iron so that it never saturates. All of those factors play not only into the sound, but they hugely affect feel.
TQR: Can you briefly summarize each model you build?
The 8 inch version of the Mosaic comes with either the stock 5F1 (Champ) output transformer or the oversize version, which nets you perhaps an additional 2 watts. You get more punch rather than volume. I also build a 12 inch Mosaic Mark II with an additional tone knob, which gives you more bass.
The Cortez was intended to be my flagship model until the Cremawheat came out. The name was inspired by Neil Young’s Suma album – you can just hear the tweed all over it. Its 12W-15W with 6V6s and it bumps up to about 18W with 5881s or 6L6s. It’s basically a straight-ahead 5E3 design.
The Cremawheat is my attempt to retain the tone and feel of a great 5E3 Deluxe, while giving you the dynamic range that would otherwise be lost in the output transformer and speaker with that amp. Those were two choke points on the 5E3, and the third being the massive amount of bass that’s being sent through the circuit, which causes it to distort so early. The other significant feature in this amp is the British-voiced Scumback speaker. It adds punch to the dynamic range, and enough bass, but not the ragged and loose 5E3 style low end.
The T35 covers the 5F4, 5E5-A and 5E7 circuits for the Bandmaster, Pro and Super. They were basically the same chassis with a couple of minor resistor changes and three different speaker configurations, and I tend to prefer the 1×15 and 3×10 versions. It’s the only fixed bias amp I offer. I like the T35 series, but I tend to gravitate toward the cathode biased amps and most of my customers seem to as well.
If you took the 2-input ’55 Bassman, which shares a lot with the Super, Bandmaster and Pro amps of that era, and cathode biased it in a 2×12 speaker format, that’s kind of where the Blue Point sits. When you pay it clean, it sounds very American in the style of a mid-’50s Bassman, and as you turn it up, you get more coloration from the British-voiced speakers. It starts to cross the Atlantic into that early JTM-45 Bluesbreaker tone, but stops short of a later Plexi amp.
The Buckwheat is the follow up to the Cremawheat. It’s a 6L6-based, 30 watt with the Scumback H-75, which is their version of the pre-Rola G12H. It has a significant amount of headroom over the Cremawheat, and the speaker produces a glassier, high-headroom tone with a bigger transformer and a larger cabinet that leaves more air around the notes. If you’re a Telecaster player, for example, who wants more headroom with just a little hair, this is that amp.
TQR: Will you build specific amps with different speaker configurations as a head or combo, and what is the current lead time for an amp?
Sure, I’ll absolutely build variations on the stock models – I actually really like the 16 inch Mosaic and I have built several of them. I want to know that I’m building exactly what a customer wants. The lead time right now is eight weeks, and I always try to keep it under three months. I sell direct, and through a small dealer network, but I do enjoy working directly with customers. Depending on what a customer wants, I may suggest a specific change to the stock circuit, and I find that interaction very rewarding Introducing another 15W–20W amp in these pages is nothing new – in the past year we’ve invested a log of ink highlighting amps like Jeff Beck’s choice of a Pro Junior, our vintage ’59 Deluxe and ’76 Princeton Reverb, the Retro-King 18W and the Trace-Elliot Velocette. Why? Because we understand that such friendly decibel levels offer adequate volume for use in small clubs, mic’ed on bigger stages, yet till fill your house, studio or practice room with a mighty roar when needed. Small amps just make more sense today for most players, but like us, you might be wondering just how many ways a smallish guitar amplifier can be designed and built to produce a genuinely unique voice and vibe. You know what you’ve already got, but what might you be missing, and at what point does your quest to discover the ultimate low power amp become redundant, at best? A fair question, and given the nearly infinite variables created by the marriage of different components within different circuit designs, we are happy to report that we haven’t reached the end of the road in the quest for tone quite yet.
Viewed within the board context of the booteek amp landscape, the Tungsten Cremawheat emerges from the box as an uncommonly attractive natural blonde. Offset with gold grill cloth, it scores big in style points without even being lit up. Nor will you find any self-conscious bells and whistles added to an otherwise classic design, as if the builder wanted to get noticed by adding the kind of stuff we seldom really use – like Selmer-style rotary tone switches, pentode/triode modes and toggled boost switches (although Carr has always done those right by bypassing the tone stack). Indeed, this amp is so outwardly attractive, approachable and comely that pulling the back panel off might inspire distant memories of an anticipation experienced in concert with a one-handed thumb and forefinger bra removal technique. (We now pause to allow a moment of fond reflection. Please take your time.) Adam Palow’s skill in assembling and soldering up a circuit board culminates in nothing less than a work of art. Flip the chassis over and the custom-wound Mercury Magnetics trannies provide further evidence of Palow’s commitment to following his muse. In practical terms, you get four inputs into two channels (bright and normal), volume/volume and tone, plus a standby switch and extension speaker jack.
Our first session with the Cremawheat was agreeable enough, but repeat visits left us with a nagging impression that something was either missing, or perhaps technically present, but not being fully reflected in the sound of the amp. Naturally, we used our tweed Tremolux and Deluxe for benchmarks, and the Tungsten sounded subdued and restrained by comparison. We tried different tubes first with no appreciable change, and that’s when we focused our attention on the Scumback speaker. Admittedly, we had suspected it from the beginning, so with the original tubes back in the amp, we connected the Celestion G12H30 70th Anniversary in our ’59 Deluxe cabinet to the Cremawheat, fired it up, hit a big E chord raking a heavy Pyramid pick over the strings slowly, followed by ten minutes of unbridled delirium. Paired with the Celestion, the Tungsten bowed up with increased volume, clarity, dynamic punch, and a gloriously rich tone that easily rivals that of our Deluxe, but with a little more added sparkle. Swapping the stock Electro-Harmonix 6V6s for a pair of RCA 6L6s brought the Cremawheat to climax with an even bigger, more imposing voice, precisely in the style of our ’59. If anything, the Tungsten offered a slightly more defined and chiseled tone as a new amp should when compared to one that has undergone a half century break-in period.
To be fair, we called Adam Palow to inform him that while we absolutely loved the Cremawheat, we were not feeling the Scumback. He agreeably acknowledged that the Scumback was indeed somewhat more subtlety endowed than the Celestion, which is why he offered the G12H as an alternative for players desiring maximum girth, power and growl. Any number of modern speakers would surely sound outstanding in the Cremawheat – but we clearly preferred the more vivid soundstage created by the Celestion when the choice is narrowed to one of the two stock speakers offered. Would we buy and play the Cremawheat? Absolutely. It now reigns among the best on temporary boutique twenty watters, and in four important respects (tone, overall clarity, availability and price), the Tungsten impressed us as an irresistible alternative to a vintage Deluxe and any and all modern replicas

After a hiatus of 45 years or so, Fender has been carefully re-entering the business of building hand-wired tweed amplifiers with the resurrection of the narrow panel ’57 tweed Twin and the ’57 Deluxe. Of course, there are scores of small amps that have been inspired by the Deluxe, and many more 5E3 knock-offs being built today in the “subbooteek” cottage industry comprised of solo solderers who build in their spare time and often put their work up on eBay. For some cost-conscious players, a tweed Deluxe for $600–$800 is a deal that cannot be refused—even if the amp was wired up by an unknown tonehead on a basement workbench in Akron. But Fender is Fender, and while they chose to ignore the thriving boutique market for hand-wired tweed circuits that blossomed in the early ’90s with the appearance of Victoria, they have not forgotten how to put an amp together, and in the case of the Deluxe sent to us for review, it stands apart from all the rest with a very unique voice.
We asked Fender’s Shane Nicholas and Sergio Hamernik at Mercury Magnetics to explain the process of natural selection that evolved during the development of the ’57Deluxe….
TQR: Describe the process in which your design team evaluated various vantage examples of the 5E3 Deluxe, and how widely the actual sound of the vintage amps you listened to varied, specifically?
Shane:There are several guys here at Fender who own old amps, and we also have friends who do. When we were ready to begin the’57 Deluxe project, we brought in a few original vintage examples, and a couple of “boutique” versions of this type of amp. We listened to all of them with various guitars, and listened to each amp chassis hooked up to the others’ cabinets. Keep in mind that every amp—especially 50-year-oldones, will sound a little different than another one of the same model. It’s pretty well documented that Leo Fenders some times changed components “on the fly,” while the official schematic documentation would be updated later. My old Deluxe might have been built with some different stuff than yours, even though they were both “stock” 1957 5E3models. Then add in aging, abuse, repairs, etc., and it’s a wide target that needs to be narrowed. For example, we had one amp here that was much more distorted sounding than the others, so unless you are only laying 1951 Howlin’ Wolfstuff, you probably wouldn’t like that amp as much. For me, the ideal is an amp that gives a beautiful clean tone with the volume set low, and a dirty, harmonically rich tone with the volume set high. You should also be able to set it on, say, “5” and control the amp’s distortion by simply varying your pick attack. We decided that one of the old ’57s was the most desirable example of a 5E3 Deluxe, and we used it as the golden sample.
Once we got to this point, project engineer Nick D’Amato really got down to business. The final schematic and components we chose were basically picked so the prototype would sound as close as possible to our golden sample amp. Obviously, we use new parts, not 50 year old stuff from a flea market or whatever. We also had to make a few changes in order to pass modern worldwide safety regulations; things like shielding, ground wires, and the three-prong power cord, which negated the use of the old ground polarity switch. We put a Standby switch in its place, which is a good thing. These changes don’t really affect tone, but they do reduce hum and improve playability.
We also decided to go with 12AX7s in the preamp, even though the originals were designed with the 12AY7 in the front end. Our thinking was, not only is the 12AY7going to be tough for us to get in quantity, but many players in fact prefer the 12AX7s higher gain. If you are playing ZZ Top stuff, for example, you’ll probably prefer this. The12AY7 will work, however, so some owners will buy one and stick it in their amp.
The transformers are also a crucial piece of the puzzle. We auditioned quite a few prototypes, and some of them were too efficient or too distorted, etc. One of the vendors we contacted was Mercury Magnetics, whom we’ve worked with in the past They sent us five different power and output samples, each based off an original transformer set found in a vintage Deluxe amp. During A-B tests, one of these closely matched the OT in our golden sample amp. We worked with Mercury to make a few tweaks, and soon we were positive we had the right transformers.
TQR: How many different types of speakers did you consider?
Shane: Well, the original Jensen in my old Deluxe really sounds and looks perfect, like you’d expect. We found that the new Jensen P-12Q sounded close enough, so we stopped looking. In my ten years at Fender, I have discovered that no matter what speaker we supply in a tube amp, a certain percentage of customers are going to try something else. Celestion, Jensen,Eminence, and boutique guys like Weber all have their supporters and detractors. It’s human nature to tinker with your machinery, and a speaker swap is one of the easiest mods you can do to an amp.
Now, having said all that here’s where it gets fun. One of the boutique amps we tried happened to have a Celestion Blue Alnico speaker in it, and it sounded very good. So we tried that speaker with our prototype 5E3 amp, and said,“OH MY WORD!” I had heard that speaker before in different amps, but this combination was stunning. The amp became a lot louder, for one thing.We thought for a minute about using this speaker in the ’57 Tweed reissue, but it’s not really the authentic, original sound or look. It’s also a lot more expensive. So, we remained sold on the Jensen, but when we developed our limited edition, black lacquered version—the Fender 57 Amp—we decided to equip it with the Celestion Blue.
TQR: What are the unique challenges involved in building hand-wired amps, compared to those with a printed circuit board?
Shane:Making it look and perform like the old amp while using readily available parts that we can buy in quantity. I am a stickler for performance, but if our customers didn’t care to look inside, we wouldn’t worry about the looks of the components and wire so much. For example, Alexander Dumble told me he likes our new ’57 Deluxe, and was surprised that we used such heavy wire in the chassis, as it’s really not necessary. We can’t pass modern safety regulations using cloth wire, so we got the next best thing. I’d also like to mention that, while we build higher quantities of hand-wired amps than all the other boutique builders, it’s still a very small number compared with the number of PCB amps we build, like our Hot Rod series and all the sold-state models. Our factory estimates about eight times the labor in a Vibro-King versus a ’65 reissue amp with a PCB.
TQR:We would assume that Fender has a separate group of employees devoted to building the hand-wired amps.
Shane: We do have the hand-wired team in a separate area in the factory. They are highly trained, patient employees who take a lot of care with these amps. Most of them are women, same as Leo’s day, maybe because they tend to be more patient than us dudes. And women’s hands tend to be smaller, making it easier for them to run wires and solder connections in the tight confines of the amp chassis. I don’t know the training regimen off hand, but I believe many of them cut their teeth on guitar wiring before moving on to amplifiers.
TQR: With the tweed Deluxe in production, are there plans to develop additional hand-wired Fender models of the past?
Shane:Yes. The list of great old Fender amps begging for reissue is a long one!
In case you don’t know, Mercury is known for having acquired and cloned hundreds of stellar vintage transformer sets that com-prise their ToneClone and Radiospares series…
TQR: How did you become involved with the development of the 5E3 specifically?
Sergio: It call came about as a follow up to the ’57Twin-Amp reissue project that we were a part of a few years ago. Mercury designed and supplied Fender with the transformers for those amplifiers, which was a very successful endeavor—so much so that Eric Clapton made them his main amps for his own tours and the Cream reunion tour.The momentum started by the ’57 Twin-Amp project quickly created a demand for some sort of follow-up amp in this positive vibe, and Fender’s decision to reissue the 5E3tweed Deluxe came as good news to us. It is probably the most copied circuit on the planet, and I couldn’t think of abetter project to sink our tranny designer teeth into.
Years ago the late Ken Fischer, of Trainwreck, told me that the Deluxe was an early inspiration for him to get into amp building. He went as far as to refer to the Deluxe circuit as the cornerstone of the boutique market. It’s a truly different dynamic when the company that started it all wants to reintroduce a benchmark in amplified guitar tone, and especially when their goal is to make the amp sound as fresh as it did when it was first launched. We’ve worked for decades acquiring our extensive library of transformer designs that originate from variants of pre-production to pilot runs of many vintage amps, so amplifier companies often consult with us because we’re a small but dedicated group just nutty enough to be the conservators of such things.

Where did you get the idea to start an amp company?
It was the K&F that got me started. Working at Fender and knowing the entire lineage, including the K&F era, which is kind of separate, it was really intriguing to see what kind of things he came up with. Because it was so rare, the K&F was really appealing to me.
How did you discover this cool original gear while at Fender?
People would come in with things that were not in regular production and would want to have things done and have items reproduced, and people would come in for repairs too. It was a nice influx of cool equipment coming in, and we would turn around and reproduce it to the best of our ability. One of the first pieces we did while I was there was the “snake-head” Tele set, the first regular Fender-style guitar that Leo built.
 Doesn’t that predate the Nocaster?
Doesn’t that predate the Nocaster?
Yes, in fact I think that guitar was a ’47 or ’48. It had a four-piece pine Telecaster-style body, two inches thick with a small, black Bakelite pickguard, volume and tone control, and one bridge pickup. The snake-head headstock was the style he was using on his K&F lap steels, so it had three-on-aside tuners, with a solid, fat, maple neck with no truss rod — he hadn’t thought about a truss rod yet! They only made a few of them, and they were made as a set with the woody Pro amp.
So, did you put truss rods in the reproductions?
No, but they are big, round, C-shaped necks, and they’re quarter sawn, so they don’t move around too much.
There are actually guys who believe that necks without truss rods sound better.
This guitar is really neat-sounding because we used antique pine. One of my first jobs there was to rough-cut these old pine boards, glue them up, and plug and fill nail holes. Looking at these old-style guitars and amplifiers in comparison to what was being manufactured at the time, I saw a night and day difference. These have a style to them that nobody does any more.
This got me started thinking about K&F. If the circuit for the woody Pro was primitive, then the K&F amp circuit was even more so. The Pro had 6L6s and a push-pull output, and a 15″ speaker — a field coil speaker, which we had a lot of problems with. The K&F amps didn’t use field-coils and were permanent-magnet.

Give us a little background on K&F.
It was Doc Kauffman and Leo Fender. The information on K&F varies, so I can’t give a perfect history. They started around late 1944, and ran probably to the end of ’45 or early ’46, then they stopped making these in mid-1946. Leo had done some really interesting things — he had designed an automatic jukebox and little P.A. systems, and he was working with his radio company. Then, he had an idea for these guitars. He started making them and it became popular enough that he needed a larger investment; Doc didn’t think he could invest in something that looked like a hillbilly guitar, and at that time, that was the type of music played on them.
I remember even up until the 1960s, many jazz guitarists looked down their noses at these and told us, “When you grow up, you’ll get a real guitar,” meaning something more traditional, like a Gibson archtop.
Yeah, so Doc left and the K&F company was dissolved. Finding pieces from that time period is hard because there’s no record of how many were made and there were no advertisements for them. I do have some pictures from George Fullerton that Doc’s son gave him of the first piece that they put together, which is nothing like the ones that went into production. It’s very beautiful.
 Did you get to play that original Tele that was copied for this run of instruments?
Did you get to play that original Tele that was copied for this run of instruments?
Oh, no. The story behind that guitar was that Leo was a huge stickler for not keeping prototypes around. There were two of those — the first one was cut up and the second was thrown in the trash. George pulled it out of the trash. He was young and had just started working with the company; he was a guitar player and this was his creation too! He and Leo went to little bars and shows and listened to players. Without telling them what they were up to, they asked the players what they would want in a guitar, which became the basis for their business and designs: being able to change small parts out easily and being able to easily change the neck on a guitar. There was a bit of a stigma attached to their early instruments because they weren’t craftsman pieces — they were functional instruments.
Yes, they were outside the instrument crafting tradition. This was a modernist piece of design, rather than following classical instrument-building traditions.
Exactly. So when I started researching all the K&Fs, I talked to George who was there just after Doc left, and I got as much information as I could from the closest source. Strangely, though they made guitars and amps in sets, many of the guitars still exist while most of the amps do not. I figure that the guitar is a functional piece and all you have to do is change the strings, but if you have an amp go out, it might have been easier to just go buy another amp.
Was it through the process of reproducing old gear, and speaking with George Fullerton, that you became interested in the 1940s K&F amp?
Yes, that amplifier in particular because it was so simple and because the circuit was kind of the predecessor to the Princeton, but instead of having an 8″ speaker like a Princeton, it had a big, large-magnet, alnico 20-30 watt 10″ speaker. This was late ’44 or early ’45, and these amplifiers were made from military surplus parts, so they were all different and had this unique industrial look about them. Design-wise, it wasn’t made to be the prettiest thing out there — it was made to be functional.
So it was just “The K&F Amplifier” and they only made the one model?
No, see that’s the thing, they made one, and we know the record shows from Doc’s writing on the pictures I have, that the first one they made was beautiful! It had wooden sides, a grille cloth that was embroidered with K&F on the front, and a 15″ speaker. The photo says, This is the first K&F [lap] steel, and this is the first amplifier in the U.S. with a hanging chassis and hanging tubes.” Before that, everything was put on the bottom of the amplifier and the tubes all sat up.
And that amp is gone now?
Yeah, in John Sprung’s book, Fender Amps: The First Fifty Years, he wrote that this amp was made as a custom, one-off piece, and it is likely gone now, since the only pictures we have ever seen of it were the from the 1940s.
That would be a fun one to reproduce, wouldn’t it?
Oh, it would be amazing. There was an article in the October 1998 issue of Guitar Player with a 15″ K&F — the style of the K&F that I am reproducing. It was the same cabinet shape, just larger, and it is the only time I have seen a 15 other than that one custom one-off piece.
 So what you had was three or four amps, all without names or model numbers which were essentially prototypes
So what you had was three or four amps, all without names or model numbers which were essentially prototypes
Yes, they were “if this works we will make another just like it” sort of deals. There were two basic models that you see in published pictures. One is the 8″model that looked like a little lunch box. It had one volume knob and one or two inputs, no pilot light, no fuse, and the cord coming straight out — that was it.
The other is the 10″ model, which is the one I’m reproducing. It had two inputs, no fuse, no pilot light, one tone control, and either one or two volume controls, and two channels — which was something completely new. Each channel ran on one half of the input tube, which is what Fender did until the Blackface era in the ’60s.
It’s not a large amp at only 5-6 watts. The speaker was an unknown Jensen model that had a large, plug-style alnico magnet instead of the horseshoe magnet. I am sure every example varied because the parts all varied — the knobs, transformers, everything. The transformer on the one I am reproducing was a replacement transformer right out of an Allied catalogue made by some unknown manufacturer.
How did you originally come in contact with the amp you decided to reproduce?
I worked with Geoff Fullerton at Fender, who became a good friend of mine. Geoff is George’s son, and was Leo’s personal assistant at G&L for several years. He was a builder and engineer there as well. George’s father used to work at Fender in the wood mill where he ran this huge ripsaw, which George, Geoff and I also ran, so I had become good friends with the family.
George is a wealth of information and a really interesting man to talk to. He has great ideas about how things were done, the reason things were done, and craftsmanship. Even though his guitars were not traditional, the craftsmanship that went into them was impressive. They case-hardened every single one of the screws that went into a guitar, so if you had to repair it, you wouldn’t strip out the threads. Nobody does that kind of thing anymore because it is not cost-effective.
When I talked to George about the amp, he told me about one at the Fullerton Museum owned by Phyllis Fender, Leo’s widow. As he described the amp to me, I decided I wanted to take a look at it. Phyllis said sure, so they pulled it out of the museum for a day. I looked at it, taking every picture and measurement I possibly could. I worked with what I had, but it wasn’t enough to do a reproduction. Later on I was able to go back, and they let me take the chassis down and measure every single component. One thing I couldn’t do was turn it on.
You were able to disassemble this old amp down to the component level?
I was. I took my meters down there and measured everything. Not only did I measure it, but I cross-referenced it to the color code because those resistors and capacitors are 63 years old now and have drifted a lot. One of the things I noticed is that he used many of the components because they were the only things he could get. They weren’t exactly the right value for the position they were in, but he put them in there because they were close enough and that’s what he had.
 So, I’m looking at it, and George leans over and says, “You know, you’re the first person who touched the inside of that amp since Leo; you’d better be careful!” Because no one had touched it in all those years, the chassis, being made of steel and zinc plated, was pretty much pure white and powdery — I wasn’t about to leave my fingerprints in it!
So, I’m looking at it, and George leans over and says, “You know, you’re the first person who touched the inside of that amp since Leo; you’d better be careful!” Because no one had touched it in all those years, the chassis, being made of steel and zinc plated, was pretty much pure white and powdery — I wasn’t about to leave my fingerprints in it!
Are you going to reproduce the zinc plating and everything?
Oh yeah, but I’m not going to relic it or try to make it look old.
Are there any ground issues getting through the zinc?
Yes, you have to grind away the zinc to get to the steel. And that was one of the things; there’s no circuit board, it’s all point to point, and whatever had to be grounded was run straight to the chassis right there. It was function over form.
What year was the original produced?
I don’t really know if it is one of the earlier or later ones, although I think it is earlier. There is a kind of complex cutaway on the top of the amplifier and a relief on the cord panel that is pretty much decorative. Those two things are also on the 15″ amps that we know were the first ones made. Later examples don’t have either of those features on them, so it is likely an early piece.
Did your experiences at Fender and taking apart the old K&F amp lead to your decision to start an amplifier company?
The K&F thing led directly to my own amplifiers. That amp was amazing and cool, but it was so rudimentary. Boutique amplifiers are becoming a bigger business now and I though it would be interesting to see if I could do my own interpretation of the design.
I was looking at all these beautiful Fender guitars that we were making, the amazing Custom Shop guitars with custom finishes that people wait years for. There are some really nice-looking amplifiers out there, but most of them look like big Tolex suitcases.
It all started me thinking about something that was small enough that you wouldn’t worry about it getting banged around, with the form plus the function, and replicating some of the beauty of the guitar finishes. That really appealed to me – no one was doing that. Finishing it like a guitar, the correct way, is such an art. I wanted to make them so they would match people’s prized instruments.
 Over the years, guitars and their finishes have gotten more elaborate, but you aren’t doing that with the new Model 10; it is using simple shape, texture and color for the amplifier, rather than the busy style of many expensive guitars.
Over the years, guitars and their finishes have gotten more elaborate, but you aren’t doing that with the new Model 10; it is using simple shape, texture and color for the amplifier, rather than the busy style of many expensive guitars.
I started out spending hours designing cabinets, and the right one just hits you. This one was simple; it effectively gave room for my logo, but with some different elements. I have 1″ radiuses on the corners instead of ¾”, which makes the amp look more spherical, instead of looking like a big square
It gives it a softer, more attractive appearance.
I started the design of the amp with the cabinet, and I got that nice angled swoop to the front, which was simple, not complex — you see some of the amps from the 1940s that had great grilles on them, and some were so complex. Once I got the design for the cabinet down, and I knew that I could physically produce it from a woodworking standpoint, I knew how much space I had, so I could work on the chassis and circuit layout.
Tell me about the Model 10’s circuit and electronic design, and the sounds you were going for.
Well, George introduced me to Bill Sterle who started working at Fender around 1960. Bill is an audio engineer who designed a lot of the original Blackface amps.
Having someone who was there and who designed amps telling me why they made certain decisions is so much different than starting with copies of what Fender, Gibson, or Marshall did. I learned distinction between the amps Bill made and the Fender amps of the 1950s, which were the easiest and simplest designs. The Blackface-era amps were much more complex designs and they were really trying to do different things with the preamps to keep them cleaner.
When Bill was designing things, he stressed that distortion is your enemy — that’s the school of amp design he came from. You have to have the cleanest representation possible. I went to Bill’s house for hours and he would describe everything from tube heater circuit design to what you want to get accomplished in the preamp section, the phase inverter section, and the power section. He told me once you get going on the tone controls, you can go crazy because there are so many variations in tone circuits — not only what you use, but where they are placed.
I wanted to have a 10″ speaker in there. A 10 just has a clarity that you cannot get from an 8″ speaker, and I didn’t want to go as big as a 12. 10s have a really neat sound to them if you find the right one. I knew it was going to be either a small, single-ended design or a cramped, push-pull design. I ended up starting off with a small single-ended design.
So, design wise, you met some of the original guys who developed modern guitar amps, and took it from there, as if you were in that era.
Oh yeah, and every single element that was put in the amp was based on what I was trying to accomplish in the circuit, not based on something I was trying to copy. My initial intention was to make it really straight and clean, without a ton of bells and whistles. It is a single-ended design with a 6V6 power section and a 12AX7 preamp tube.
I looked at a lot of Internet message boards for guys who are building amps, and for players in general, to find out what kind of modifications they were making and what they wanted out of an amp. I tried to keep it really simple and clean, but I did put in a few things that I thought would expand the tone a little more.
 Is there a tube rectifier?
Is there a tube rectifier?
No tube rectifier in this. In such a small, single-ended amp that putting one in would be more of a novelty than anything functional. Not putting one in allowed me to use a smaller power transformer and to clean up the power and make it more stable, along with giving me more space to do other things in the chassis. Also, when I went back and talked to Bill Sterle, he threw his hands up and said, “Tube rectifiers are absolutely worthless!” [Laughs]
My impression is that stout, well-built power supplies produce robust tones, especially at high levels. When you are pushing the amp, and you’re not clobbering the power supply, the amp doesn’t freak out as much. If I want a little sag and compression, I use a compressor!
Well, yeah. It’s all relative though, because there is a ratio between the voltage and the current that the plates see. You push harder, sand the plates, and try to draw more current. If the current isn’t there, then there is going to be a difference in the tone.
I started with a solid-state rectifier and that is the only solid-state piece in the amp. In the preamp, I used more of a Blackface preamp design, where I split the 12AX7 in the middle because the amp only has one channel. I do have two inputs on the amp, but one is just hotter than the other.
So there are only two tubes in the amp?
Only two! It’s simple — there is just a treble and a bass control. With all passive tone controls, if you use the control, there is a certain amount of insertion loss, so on bass control I put a switch so you could remove the tone controls from the circuit completely.
The Model 10 has the standard volume, bass and treble controls; then there is the switch. What does it do?
It takes out the negative feedback loop. You turn that off and bypass the tone controls and it will crunch just like an early tweed Champ. Even with only two tubes and three knobs I wanted to be able to have a range so it isn’t just for one style of play; it is an amp that you can play around with and get a cool tone out of.
It has an amazing array of tones for having so few controls.
I have designs of every shape and size, but this is where I wanted to start. In the larger models, I am going to do a 15-20 watt amp, and I may do as much as a 30-35 watt one as well, though I don’t want to come out with a 100 watt monster.
I think people are starting to re-evaluate how much wattage is really needed.
You know, one of the many helpful things I learned from Bill Sterle was how to test everything correctly. Lots of amp makers out there will say, “This is a 5-watt amp,” and that’s what they assume because a similar one was made by Fender, but Fender tested where the wattage comes up just before distortion, on every one, and that’s how we test as well.
The Model 10 puts out almost exactly 5 watts. It has a cathode bias power section and I go through and measure every single one of those tubes and every single output section of each amp to make sure it is right for this design. I don’t want to run these as hot as I possibly can to get every last watt out of them, because it is hard on tubes. I offer NOS tubes as an upgrade, and they are not making any more of them! I run them right in the middle where you get great tone and good longevity.
What tubes have you been using?
Right now I am using Electro-Harmonix preamp tubes and JJ power tubes. I think the JJ 6V6 is a really neat tube. They can handle a lot of plate current, and they sound good.
If somebody wants a Model 10, how long would it take?
I have all of the parts ready to go, but I have a six to eight week lead time on the custom-colored cabinets, including shipping. It takes about four weeks for the paint to be completely finished, because it has to be perfect. It is a guitar finish on the Model 10 and it’s done just like any expensive guitar finish. The amps are built to order, though I may stock certain colors here and there.
 It’s exciting to see the founding of a company with such an amazing product. Do you have a price set for the Model 10?
It’s exciting to see the founding of a company with such an amazing product. Do you have a price set for the Model 10?
It looks like the Model 10 will be $1050, at least as an initial release price.
You spoke earlier of having several color choices and perhaps some clear finishes on nice wood available.
The cabinets right now are poplar for the solid colors, and ash or alder depending on whether the finish is a blonde or sunburst one, just like a guitar.
If someone asked you what your amp sounds like, what would you say?
Well, what I was trying to achieve was a combination of the tweed Champ and Princeton, combined with a Blackface Champ and Princeton. I wanted to be able to combine all four of those amps together so you could get a really grungy, overdriven, tweed tone or a really clean, clear tone with or without tone controls.
Tell me about the K&F reproduction amp, is that currently in the pipeline?
That amp is 99% done. Because this amp has never been done before, and because the parts are not off-the-shelf parts, everything is different from what is currently available. Everything had to be done from scratch; transformers had to be custom wound, and chassis had to be custom made — and the chassis are not normal dimensions by any means. The tubes are all NOS tubes, because there is no current equivalent to them.
It’s an octal socket preamp tube isn’t it — a large base and pins like a power tube? What tube is that?
It’s a 6SC7 medium mu triode and a 6J5 triode in the preamp section. Each channel gets half of that triode. It’s a pretty low-gain tube actually; it’s not overdriving the preamp circuit a lot like the later 12AX7s often do. There is also a 5Y3 rectifier and a 6V6 output tube. Both input signals merge into a 6J5. Instead of putting one channel with one preamp tube, he made two channels that merged into one preamp tube. There’s one volume control for both channels. The circuit is a lot different than a modern amplifier. Leo was doing it to see if it would be functional, and it was very rudimentary and basic.
The octal preamp tubes give a really unique sound to the amp. They don’t drive it very hard, but it does put out a pretty thunderous crunch when you want. I am keeping it as historically correct as I can, with carbon comp resistors, Mallory 150s as the tone caps, and all cloth-covered wiring, which I don’t do in the Model 10. I am not trying to reproduce a look in the Model 10, but am going for the best possible sound, so I’m using all the best components and wiring by today’s standards.
You selected the components for the Model 10 by listening to them, didn’t you?
Yes, but the K&F is a little different. It’s not wired like you would wire something today; it has series heaters, so you get that hum in there that makes for a unique sound. The only changes I made were necessary for safety. Of course, there is a fuse in this one, along with a 3-prong AC plug. Other than that, it is rudimentary in every way. The tube sockets are spot-welded to the chassis.
Did you actually replicate the spot welds?
Oh yeah! Lots of guys would have riveted the sockets in place, but that was an extra expense, so they spot welded them.
It probably had a terrific ground connection.
It does. I found an original output transformer and power transformer and had Mercury Magnetics reproduce them for me. The speaker was a 10″ Alnico plug-style speaker rated at 40 watts for a 5-watt amp, so it was way over-engineered for the circuit. Most Alnico speakers have a horseshoe shaped magnet, but this one has 2½” donut-shaped magnet. It was also used for higher-end audio and larger-wattage amps. It makes for a really heavy speaker, but it’s really neat. This Weber is the closest to the original speaker that is available.
How much is the K&F reproduction amp going to cost, and when will it be available?
I’m trying so hard to get it finished! I am talking to a paint manufacturer about the wrinkle paint we need, and if that works out we’re in business with getting the K&F out. We should be ready in October at the latest, and the cost will be about $1000.
Playing the Amps
I brought my 1987 hardtail Tom Anderson to Byers‘ shop where I got to play through the first Model 10 off the line and a K&F reproduction prototype. Here is a sample of what I heard:
Model 10
The Model 10 is a beautiful amplifier. If your favorite custom guitar builder built an amp, it would look just like this.
The Model 10 is clear and detailed in the way that only minimal circuit paths can be. Set clean, with the tone controls engaged and the feedback loop in, the highs and lows are well-balanced, the tone circuits do what you wish they would, and the result is a sound that makes you want to play more. Turn off the feedback loop and things get woollier and more tweed-like. Switch off the tone controls and the amp gets a more aggressive, throaty attitude going.
K&F Reproduction
The K&F reproduction amp is totally different from the Model 10 and totally different from almost anything I have ever heard. I can almost hear Charlie Christian playing one and I suspect that today’s players will find musical uses for this tone. The K&F reproduction is very big and a bit wooly-sounding, yet not muffled or dull at all. It gets pretty powerful sounding when you push it hard.
Source: https://mercurymagnetics.com/pages/news/PremierGuitar/PremierG-10.htm

HISTORY TELLS US THAT Leo Fender wasn’t much for “fancifying” things. More meat-and-potatoes than chicken and walnut curry, Leo was a simply guy, and that ethos carried over to the goods produced by his company, whose early amps were covered in tweed or plain black Tolex (for flavor, sometimes brown) and guitars were mostly slabs of wood cut with no fancy arches, curves, routes, or headstock angles.
So it’s no surprise that Fender’s’57 Amp looks nothing like anything created by Leo – and why the company touts it as something he might have built if one day he’d had a little too much coffee, caught a glimpse of a passing Caddy, and suddenly developed an eye for design. We kid, of course….Conceived by Fender industrial designer Shaw Greene and design engineer Nick D’Amato, along with Shane Nicholas, Marketing Director of Fender guitar amps, the ’57 Amp is a limited-edition, hand-wired 1×12”combo that boasts several distinct features that separate it from the company’s standard amps. If you like, call it Fender’s“boutique” amp!
From the fancy, auto-inspired split grille to its piano-black-lacquer finish, knurled control knobs, sleep billet-cut-aluminum “speedboat”handle, the black grille cloth, in terms of aesthetics this is truly a custom unit. Inside, the ’57 Amp sticks to what works – its chassis is the tried and true Fender 5E3(the technical designation for the circuit, referring to its rectifier tube)Deluxe, with top-shelf components and hand-wired construction. One of the darlings of the vintage world,the Deluxe was introduced in1948. It used on 12AX7 and one 12AY7 in its preamp, running into two6V6GC power tubes. The combination delivered some of the most harmonically rich, slightly compressed sounds ever produced by thermionic valves (AKA vacuum tubes). A medium-powered amp, it was designed to give guitarists enough volume to compete with drums and other instruments. And because it so adequately handled virtually any playing style, from clean country background strumming to all-out blues and rock, it has been used by players of all genres.
In the literature and a nicely produced DVD packaged with the ’57Amp, D’Amato talks about listening to vintage ’50s Deluxes and newer clones as they searched for a shining example on which to base the sound of their concept.
For the sake of testing the sounds of the ’57 Amp, what could serve better than a trusty Fender guitar from back in the day – perhaps a ’59Esquire? And for serious head-to-head fun, why not a gen-u-wine Deluxe from ’67? To establish a reference, we first plugged into the ’56. At low volume and playing a traditional bouncy country rhythm on the Esquire, the elder amp offered the trademark uncompressed clean tone that earn edits reputation – big on the bottom, crystal clear on the top. Really nice,and really mellow – fun… for a while. But for most players, the amp starts to groove for real when you take its Volume and Tone controls up to where the 6V6s start to growl (about6). Strumming a second-position G chord (alternating with an open G and D strings for flavor – think“Honky Tonk Women”), the Esquire teams with the amp to give all the“Ahhhh, yeaahhh” tone you could imagine, its stock Jensen P12Qspeaker dancing in the pine cabinet, delivering all of the Deluxe’s 12 punchy watts. Classic, unmistakable, with glorious overtones and just the right amount of gain and compression.
Sitting next to the ’56, the ’57Amplooks shiny, new and other-worldly, its glossy piano-black exterior in stark contrast to the aged tweed of the ’56. Its split grille does look like a badass old car rollin’ in your direction, and its old aluminum handle, cap-head screws, chrome-plated tube covers, and custom-engraved big-burl knobs lend obvious custom touches.In terms of circuit and tubes, the amp has much in common with the’57 Deluxe Amp tweed

On the other hand, if you’re inspired to run down some musty Fullerton tweed, we’ll assume you are also fully prepared to bend over ’til it hurts. Well, know this… there is little correlation between the absolute certainty that you will pay a considerable premium for an unmolested, vintage tweed Fender amp today and an iron-clad promise of awe-inspiring tone. As we’ve said before, the market value for vintage instruments and amps doesn’t carry an implied warranty… You are paying a premium for a collectable amp or guitar based solely on its collectable value; the extent to which it may fulfill its intended purpose to your dismay or delight is a crapshoot unless of course you are able to try before you buy. This didn’t matter much when tweed was $50 trash, but throwing down a minimum of two grand today is no joke.
There is less risky and expensive route on the quest for tone, which is to buy a new amp made by people who have figured out how to actually design and build exceptional sounding tools with repeatable consistency. Perhaps you are the type who is risk-adverse, unwilling or afraid to adopt an old amp that may need to be fortified by skilled hands at $75/hour. Well, we’ve found another stellar new amp, and it carries the familiar name of Lindy Fralin. No, Fralin didn’t personally build it, but it is built to his specifications and personal preferences by Vintage Vacuum Tube Amps in Waldorf, Maryland, which is close enough to Lindy Fralin’s shop in Richmond, Virginia to have fostered a very productive collaborative relationship.
Lindy Fralin is one of the best known custom pickup makers in the country and an experienced guitarist with an extensive collection of vintage amps. But despite his fat collection, he found himself craving things that weren’t collectively found in any one of his vintage amps. Fralin wanted clean headroom at volume levels that could hang with a band in a small to medium-sized club. He also insisted that such an amp be portable enough to be effortlessly carried up and down the stairs in his house and back and forth to gigs. He wanted reverb, and a smooth, musical voice that was compatible with all of his many guitars, and the amp had to be a looker in a dignified, classic sense — not too plain or gaudy in an effort to appear different or unique.
Fralin and the two founders of VVT spent months working on various prototypes, which involved several rounds of experimentation with custom transformers built by Mercury Magnetics. Once the basic layout was determined, different caps, resistors, tube configurations and speakers were tested, and work continued until Fralin finally heard the sound and feel he had been craving in his head.
The result is a remarkable 30 watt, 1×15″ cathode biased beauty that can run on dual ^L^s for maximum headroom or 6V^s for slightly faster breakup. Features are simple and straightforward with just a bright switch, volume, treble, bass and reverb controls. We ran the Fralin through its paces with all of our usual test guitars, and we were consistently impressed with the sound of them all, as well as the hug spring reverb, loads of clean headroom and subtle distortion at higher volumes that adds sustain without substantially altering the beauty of the fundamental note. As we played Fralin’s amp, reoccurring visions of Peter Green’s brilliant tone came to mind… clean, exceptionally smooth, warm and round with the perfect edge, enabling the guitar to alternate between sweetness and urgency as dictated by the song. Our impression was also echoed the the other guitarist in Delta Moon, Tom Gray. Tome plays slide using acoustic Weissenborn-style guitars loaded with a Sunrise soundhole pickup. Prior to hearing the Fralin, Tom’s stage rig consisted of a Blackface Pro reverb head paired with a separate 1×15 cabinet and an Avalon preamp identical to that used by Clapton for his acoustic guitars, live. After Tom played the Fralin amp sent to us for review, he bought it, and now no longer even needs the Avalon.
Aside from looking good and weighing barely 30 pounds, Fralin’s amp incorporates an “Integral Beam Diffuser” — a wooden cross-piece cut out of the baffleboard that bisects the speaker behind the grille cloth, diffusing the sound waves as they come off the speaker cone. Fans of larger ’60s Supro amps may be familiar with a similar cross-piece found in those amps, and it does indeed produce a sound that is less beamy and linear (especially helpful when you’re crammed on to a tight stage with the amp on the floor). You really can hear it better.
VVT’s Fralin amp is simply a compact, lightweight, heavy-duty gig monster, and it definitely deserves your attention. The Weber Classic Alnico 15 thrives on every frequency you can throw at it in the Fralin, and we recommend this amp without reservation for blues, heavy rockin-blues, jazz, country, swing… everything but hard rock and metal. For that, check out the other amps built by VVT.
Source: https://mercurymagnetics.com/pages/news/ToneQuest/_2006/TQRDec06.htm

Of course, the perfect segue would now be to decipher the “special” nature of the original output transformer in Neil Young’s narrow panel tweed Deluxe, providing you with a timeline in which these happy accidents appeared, or better yet, a source for clones of thee special gems via, say, Mercury Magnetics. Sorry… we asked, and while the guys at Mercury had heard the same story about the output transformer in Neil’s Deluxe, we can’t offer any definitive clues to what Larry described as “the most perfect way form.” However, we can immodestly suggest that you snag a TQ Clarksdale [ed. note: built using custom Mercury Magnetics trannys]—a faithful clone of our original 1959 DeArmond 1×12. It’s Neil’s amp in spades and he doesn’t even know it. The first batch of ten have been shipped and a gutsier, louder or more soulful 20 watt 1×12 has never been built. We can’t (and don’t) take credit for the original design—that belongs to an unknown engineer at Rowe Industries in Toledo, Ohio circa 1959—but we can state without any doubt whatsoever that the Clarksdale nails the tone and attitude of the original, and the original is the most impressive 1×12 we have ever heard. It’s got more bottom end and stronger mids than a tweed Deluxe, and where a Deluxe folds up, the Clarksdale roars all the way to “10.” Ain’t no quit in the Clarksdale, and like Neil Young’s Deluxe, a lot of the mojo is found in the DeArmond’s mammoth, original output transformer.
With Young’s legendary tweed Deluxe off the board, we chose to put the vintage Vox AC50 Larry provided for Frank “Pancho” Sampedro on the Ragged Glory tour and recording sessions in play. Now, for those of you who tend to shy away from the potential complications that 40 year-old amps can present, the tale that follows will not inspire confidence, even though in the end, we did reach the promised land.
We found a 1965 gray panel Vox AC50on eBay with a “best offer” option. A search of previously completed auctions revealed that vintage AC50shad recently sold for anywhere from $900 to $1600 (more for the earliest, small box candy panel models with tube rectifiers). Since Larry’s “Pancho Vox” was a mid ’60sgray panel with silicone diode rectifiers, we made an offer of $950 for the ’65, which the seller accepted.So far so good. When the amp arrived from Florida,however, we immediately noticed that the chassis had dropped inside the cabinet. Vintage JMI Vox chassis are mounted on a plywood shelf that allows the amp to slide in and out of the cabinet, and due to the seller’s pathetic packaging job, the plywood board in the AC50had splintered and cracked beneath the weight of the chassis. The shelf was shot, but since a cursory fire-up led us to believe the amp was in good working condition as advertised, we asked for and received a $100 credit and cut a new plywood shelf for the AC50from a reproduction AC30 cabinet we had used to house a vintage ’63 AC30head. Piece of cake, and a very quick and proper fix.
In the interest of authenticity, we also ordered a 4×12 cabinet loaded with aged Celestion G12H30s (Hellatones) from Avatar Speakers. They were running a clearance sale on loaded 4x12s for just $378 and $49 shipping, so we bit, and people, this cabinet kicks the living shit out of our vintage Marshall 4×12.
With the cabinet delivered, we were anxious to uncork the AC50at full roar, and we did—for maybe five minutes. The thick sound of the Vox filled the room, the house and the block with a gorgeous,incendiary bloom through the Avatar cab and our blacktop Les Paul, until the joyous noise was suddenly contaminated with a most noxious and fear-some popping, fizzing and spitting, while we sighted a glowing red spot on the plates in one of the Svetlana EL34s. Not good. Off to Bakos Ampworks….
After an hour of probing on the bench, Jeff asked,“Do you smell that? Man, I think the output transformer is smoked. It’s probably been going out for a while.” Jeff patched in a substitute which eliminated the crackle-spit and confirmed, “It’s toast.” We immediately punched the number for Mercury Magnetics, and with our print deadline looming large, we had the Vox tranny shipped 3-day UPS from California. Jeff popped in the Mercury ToneClone tranny and replaced the original silicon diodes with FREDS. We also A/B’d an older pair of original “Winged C”Svetlana EL34s with a matched pair of NOS TeslaEL34s acquired from KCA NOS Tubes. At $80/pair,the Tesla’s are reportedly comparable to NOS Mullard sat more than three times the price. We also installed two lightly used Mullard ECC83sin the Normal channel and a spare NOS RCA 7025andNOS Teslain the Brilliant channel. But we were still missing an essential ingredient in the “Pancho” rig….
With the Vox AC50 brought back from the brink and the ’57 Junior found, we were finally poised to experi-ence Ragged Glory. We prudently set the volume controls for both channels of the Voxon “7,” following Larry’s recommendations for tone controls—treble dimed and the bass low. We’d ease into “10” on the volume controls later…. With a flick of the toggled tripwire the Vox lit up, and within 10 seconds the P90 was humming through the four Hellatones. We stepped back a few feet, brought the volume control on the Junior all the way up, turned away from the four twelves and cut loose with a tight, slashing chord progression out of E major. Digging deep into the Junior, the Vox responded as the twin EL34s became fully inflamed, gorging on 430 volts. The tone was thick, complex and gloriously ragged with a clarity, punch and trebly character that masked nothing—the perfect burning, churning, flannel and leather rhythm tone. Hit the low E string on a fat E major and it holds…. Come over the top with an upstroke on the E and B strings and the Vox responds with a gorgeous, penetrating cymbal splash that hangs as long as you wish. Need a dash more mids? Dial back the tone poton the Junior, Pow! There it is. Thanks to the FREDS, the entire rig breathes with an extraordinary touch sensitive feel, and even on “7” the Junior could easily be coaxed into howling cries of polyphonic feedback. After 15 minutes, we reached over and dimed both volume controls…. Now we were welding some very serious shit—Mississippi Queen meets Powder finger…. And this was 50 watts of classic, vintage Voxtone, mind you…. Harmonically richer, better endowed and far less linear and one-dimensional than a vintage Marshall—a cross-bred beast with a level of gain, distortion and raw heat far beyond the capabilities of any other vintage British amp unaided by a pedal. The tone, the vibe, the drama of this amp is stunning, and it left us wondering why the vintageAC50 gets so little respect. We can think of no other vintage or current production amps that do what the Vox does. Not one. Of course, your results could vary, so here are a few tips for you brave souls willing to take the plunge.
Don’t be fooled into thinking that the Voxis solely a“rock” amp. Kid Ramos blew us away at a blues gig playing an AC30with a Fender reverb box, and his was one of the best blues tones we’ve ever heard anywhere. Expect the same from an AC30.
Do not fear replaced transformers. You’ll pay less for the amp and the ToneClone replacements from Mercury Magnetics will outperform many tired originals.
Expect the unexpected and coolly deal with it. Voxamps aren’t Fenders—things like speed nuts on the chassis for the cabinet mounting screws are often missing or broken, but they can easily be replaced.Good tubes are also essential, but not every brand will provide reliable performance or the best tone in aVox. You must also exercise extraordinary caution around the AC50when handling the chassis outside the cabinet—even when performing simple tube swaps. The preamp tubes are mounted directly above two uncovered filter caps that remain hot even when the amp is unplugged. One slip and your Quest for Tone could be over.
Plan on investing in a thorough checkup by an experienced amp tech who can deal with cold solder joints, degraded components, old filter caps and proper biasing, before your amp takes a dump. Recommended amp techs follow, along with contact info for Mercury Magnetics.

Decades ago, practice amps were effectively no-frills versions of their bigger brothers. Even so, those little amps of yesteryear became something magical in the studio. From Jimmy Page and his Supro to Joe Walsh and his Fender Champ, getting big sounds from little amps became the stuff of legend and a go-to approach for recording. Crimsontone Amplifiers embraces this philosophy in a big way—only two of the seven amps the company offers are 20 watts or more. Their newest amp—the 4-watt SE Mini—is a testament to the power of small and a cool nod to the role of low-wattage amps in the history of rock ’n’ roll.
In the Court of the Crimson
At just 7.5 pounds, the SE Mini certainly lives up to its name. The cabinet is covered in a tough red tweed fabric, and it features a sporty aluminum handle for easy transporting to the studio—or a gig in the park for that matter. Crimsontone didn’t design the SE Mini with gimmicks in mind either, which is evident in the simple feature set. It has just four controls—Gain, Tone, and Master knobs, along with a tiny Gain Boost switch.
The single-ended, all-tube head is powered by a Sovtek EL84 coupled to a JJ ECC803 preamp tube and a Mercury Magnetics GA5-P power transformer for a maximum of four watts. The GA5-P is part of Mercury Magnetics’ fantastic Toneclone Plus line, which is stocked with the company’s replicas of famous power transformers from the past. In this case, it’s a faithful reproduction of the transformer in Gibson’s 1950s Les Paul Jr. combos. I was pleased to see that the output transformer was also a Mercury Magnetics model, an FTCO-M that replicates the units in Fender’s Tweed Champ amplifiers of yore.
The SE Mini doesn’t rely on modern circuit design, but instead forgoes current technologies for a traditional, handwired, point-to-point circuit. Upon pulling out the adorably small chassis, I was treated to the sight of tidy wiring held together with clean solder joints and tight mounting. And the Components—F&T filter caps, Alpha pots, Orange Drop capacitors, carbon-comp resistors, two Xicon power resistors, and a Cliff input jack—are all top-of-the-line.
Good Things … Small Packages
Crimsontone touts the SE Mini as a practice amplifier, but it excels at hitting tones in the ’60s classic-rock vein. With a Fender 60th Anniversary Telecaster and a feed to the two 12″ speakers in a Fender Twin Reverb reissue, the Crimsontone’s clean mode belted out seriously raw, garage-rhythm jangle with a dash of classic Neil Young sting thrown in. The highs are crisp and brash, with tight lows and a gritty midrange. With a Gibson Les Paul Studio, the amp accentuated the midrange and softened highs, but the amp still retained its bold essence, staying tight in the low end and having a nice, even sag. It’s not a sound for everybody, but it speaks in the raw, unadulterated tones of no-holds-barred slingers of the first classic heavy rock era.
It’s worth noting that, while the SE Mini kicks with James Gang-worthy tones, I did have to really work with my picking hand to squeeze any real dynamics out of it. That said, that’s not uncommon with most small-wattage amps, and it certainly doesn’t mean that the amp isn’t touch sensitive. But if you’re used to using a big Marshall to get your ’70s tones, the SE Mini will feel like an entirely different animal. The amp doesn’t have excessive gain or saturation to hide behind, so it assures that you hear every single mistake. The sweet sounds that come as a trade-off are well worth it, though.

This Dog Bites
Getting the most meat and bite out of the SE Mini requires careful adjustment of the Gain and Master knobs. With the Gain Boost switch off, not much grit is available from the Gain control. Rather, it acted more like a voicing control, altering the feeling and response of the tone. Most master-volume tube amps have a gain structure that changes from tighter and crisper to warmer and spongier as you increase the Gain. Without the boost on, the Gain control on the SE Mini reacts the same way, but without adding huge amounts of saturation. Kicking in the Gain Boost adds a dose of rage to the tone, and I thoroughly enjoyed playing quick double-stops and soaring country bends with the SE Mini’s overdrive-infused, high-midrange snap.
Predictably, the boost kicks up the volume a few decibels, too. And I discovered by lowering my guitar’s Volume knob just how well the amp cleans up at even the dirtiest settings. The Gain Boost adds noticeable touch sensitivity, too. I got one of my favorite tones by dropping the Telecaster’s Volume down a quarter of the way and letting my picking-hand attack determine the amount of overdrive.
If you’re looking for more aggressive tones, it also pays to keep the Master at or near its highest levels. At practice-amp volume levels, the Telecaster sounded a little thin, and understandably so—I wasn’t pushing the single EL84 enough until I moved the Master to 3 o’clock, where there was a considerable volume jump. The sweet spot on the SE Mini’s Master is just a little higher, where it retains just the right amount of definition, while maintaining ample punch. Set the Master there and use the Gain control to set the flavor of the attack, and you’ll find a load of tone variation at your fingertips. Working within this range helped me keep the Tele’s bite under control and let the raw nature of the amp’s voicing shine through.
The Verdict
Four watts may not be the right recipe for tearing the paint off walls, but the SE Mini uses a well-designed circuit and quality components to sound much bigger than it looks— especially with a few 12″ speakers at the receiving end of its signal. Crimsontone’s SE Mini is a great choice for lovers of dirty, jangly rock guitar tones. But, like tube practice amps of yesteryear that needed to be driven and played hard to achieve their fullest tonal potential, it can require a more dynamic and forceful touch to tap into its inherent dynamics. Still, there’s nothing quite like a healthy, low-watt tube amp cranked to high heaven for creating sweet, raw, rowdy sounds. In that musical category, the SE Mini is a hit.
Buy if…
you’re a fan of dirty, to-the-point guitar tones at reasonable volumes.
Skip if…
you need to be heard over a drummer or can’t abide bone-simple feature sets.
Rating…
Street $799 – Crimsontone Amplifiers – crimsontone.com
Source: https://www.premierguitar.com/articles/Crimsontone_SE_Mini_Amp_Review

Fender designed and built more than one transitional, non reverb blackface combo amp that would soon acquire reverb and a new name, including relatively small numbers of blackface Princetons, 4×10 Concerts, 1×12 Vibrolux and 1×15 Pros. We acquired a 1×15 blackface Pro, and while it ultimately proved to be an extraordinary exceptional amp, we were also reminded of the potential pitfalls that exist when buying old amps sight-unseen, as well as the potential rewards.
We found the ’64 Pro listed on eBay and bout it from a dealer after requesting a detailed photo of the chassis and circuit. Proudly described as “the best amp in the store, “the rare ’64 blackface Pro is essentially a blackface Vibroverb without the “verb.” Do we have your attention yet? Three caps had been replaced, the original baffleboard had been professionally converted to plywood with the original grill cloth remaining intact, and an on/off pot had been installed for the tremolo intensity control that bypassed the tremolo circuit when rolled to “1” with a click, adding gain that would otherwise be missing in the Vibrato channel. We pulled the JJ power tubes and assorted Russian pre-amp tubes and replaced them with lightly used,“test new” RCAs from our stash, rebiased the amp and fired up the Pro….
Sounded like shit. We had been here before with a dead-mint ’64 Vibroverb bought years ago that had passed through a certain amp guru’s hands in Pflugerville, Texas.How could a vintage Fender sound so bad we wondered? Turned out that the value of the bright cap on the Vibrato channel had been changed on the Vibroverb, rendering a thin, scalding tone that would have given Ed Jahns fits, as it did us. Changing the bright cap back to spec immediately restored the Vibroverb to its rightful pace in history, but the Pro had other problems….
The baffleboard swap and added switch on the tremolo intensity control were clues that someone had also spent time troubleshooting the amp, probably trying to detect the cause of the Pro’s weak output, thin tone and curiously harsh edgy distortion. The amp just didn’t sound right. We pulled the original, reconed Jensen C15N dating to 1964 and subbed in an Eminence Legend, but the Pro still sounded choked-off, linear and wrong, so it was off to Jeff at Bakos Amp works on the Friday afternoon before Memorial Day weekend in a frog-chokin’ Georgia thunderstorm. When the going gets weird, the weird turn pro…..Now, this is the difference between someone who really knows his craft and a hack….Jeff plugged his bench guitar into the Pro, hit a couple of chords, issued a single grunt of displeasure and caustically observed, “Something is definitely fucked up.” With the chassis on the bench, Jeff scowled at the choppy sine wave the amp produced on his scope as he checked voltages with his multimeter. “I think the output transformer is going down slow—it measures 11 volts and it should be reading 16….” He clipped in a substitute OT from a stout old Fisher hi-fi, plugged in and hit a chord… “That’s closer to what it’s supposed to sound lie….” And sure enough, the missing lows and mids were present, the raspy treble tones were subdued, and for the moment, the Pro showed promise. We called Paul at Mercury Magnetics and ordered a black-face Pro Tone Clone replacement trans-former, shut it down and wished each other a good holiday. A week later the Mercury Magnetics replacement output transformer had arrived. Jeff wired it up, and then turned his attention o three silver mica caps that had replaced the original ceramic caps in the phase inverter and tone circuits. Jeff: “Somebody probably read an article about how these would bring the high end up, but I prefer the ceramics—always have. Besides the effect of the voltage from the old output transformer being low, these silver mica caps were contributing to that brittle tone we were hearing. They are the wrong value, and they changed the entire sound of the amp.” Jeff pulled all three silver mica caps and replaced them with the correct ceramic disc caps, and since an on/off switch had already been installed for the tremolo, we mounted the 25K mid range pot in the back panel hole for the extension speaker jack. With the Pro now thoroughly put right and the midrange pot added, Jeff hit a few chords, moved the EQ and volume settings around a bit in both channels, smiled and said, “That sounds really good. Yeah, that’s it.”
Back in our music room, the final step was to re-bias the Proat 34mA with an AmperexGZ34 rectifier and our last pair of vintage RCA black plate 6L6s, which in unused, new old stock condition have soared to $400/pair. The re-labeled Tube NOS Phillips JAN 6L6 WGBs we had tried sounded good—but the smooth warmth, exceptional musicality and deep harmonic content of the RCAs just can’t be beat, and it is a difference you can definitely hear. Smoke ’em if you got ’em….
We lit up the Pro with the ’63Fender Reverb unit and reverently smiled at the jaw-dropping tones pouring from the big Eminence Legend 15. Imagine the sound of a slightly kinder, warmer sounding 40 watt Super Reverb void of the sharp, penetrating treble presence that has sooften left our ears ringing for hours after a tumble with a blackface Super. The sound of the ’64 Pro is all Fender, with solid bass that doesn’t fall apart at high volume as the smaller blackface combos can,sweet, singing treble tones, and now… a mid range control that can gradually push the amp beyond its original, clear and liquid “scooped” mid range voice to an exceptionally thick, “mid-Atlantic” roar that unleashes heavy sustain and rich, musical distortion as only a Fender can. The Pro brilliantly complements every guitar we own, producing the essence of classic Stratocaster, Tele, P90 and humbucker tones with clarity, depth and lush fidelity that literally fills the room. Yes, there are different and equally worthy tones to be had from the British classics,but we have never heard a more beautiful sounding or versatile Fender amp—one that can range from crystalline, blackface clarity to the full burn of an early blonde Fender Bassman at much friendlier volume levels. The Pro can get plenty loud, but it’s a loud that doesn’t kill you in the style of a Showman, Twin or a Super Reverb.
The irony in this unexpected discovery has not escaped us,and perhaps the weight of it is now becoming clear to you, too. This project did not begin well, and we confess to experiencing some remorse when the Pro arrived with a few bad mods, weak and thin from the original output transformer going down, and generally just sounding very wrong. Our dismay was soon displaced by genuine enthusiasm; however, as we were reminded that this is indeed what the quest for tone is all about it. We’ve acquired absolutely bone stock amps in perfect working condition that just couldn’t tote the note, so why should we expect to buy a 44 year old amp that’s been played without it needing a little repair and restoration work? The end entirely justifies the means.
Having finally experienced the Pro’s singular, exceptional sound, we wondered what had caused it to be relegated to such obscurity among all the Fender black face amps. Like the Vibrasonic and Vibroverb, perhaps it was doomed by the presence of the single 15” speaker. Like the Pro, the blackface Vibroverb 1×15 was produced for less than a year, and with the introduction of the 2x12Pro Reverb in 1965, Fender would no longer produce a 1×15 combo until the introduction of the silver face Vibrosonic in 1972. Yet, the earlier 1×16 Pros had been Fender’s flagship amps during much of the tweed era, and in 1960 the 1×15 brown Pro ranked second only to the1x16 Vibrasonic in the Fender catalog. Somewhere along the way, the 1×15 combo had clearly fallen out of favor with Fender, guitarists, or both, and given the short life span of the Vibroverb, even the addition of reverb couldn’t save it.
Twenty years later, Stevie Ray Vaughan elevated the Vibroverb to hall of fame status, otherwise, the 1×15 com-bos seem to have been perceived as “uncool” for anything bug jazz and blues, as if wearing a jacket and tie were required to play them. The Pro is a great blues amp, but it’s also a great rocker, and equally well-suited for jazz, pop and country. With far more clean head room and power than any tweed Pro and much stronger distortion, sustain and dynamic character than a brown Pro, the blackface Pro reflects Fender’s ongoing pursuit of more powerful, cleaner sounding amps, but unlike the black face Bandmaster, Tremolux and Showman, and Pro can really rock the house cranked. We suspect it’s a single 15 and missing ’verb that throws people off today, yet in’64 Pro shares its DNA with the ’64 Bassman and all the highly prized blackface combo amps, including the Deluxe Reverb, Vibrolux Reverb, Super Reverb and the heavily prized and hyped Vibroverb.
The contrast between the Vibroverb’s Holy Grail status versus the lowly blackface Pro simply underscores how easily we can be blown off course by what isn’t hyped on the Internet or in print, and by the powerful logic that suggests if anything 44 years old is truly noteworthy, “we” would already know about it. Well, apparently “they” don’t. But you do. Blackface Pros can be found for $1 500–$2,000,with originality and overall condition driving prices accordingly. Like the Deluxe, we wouldn’t buy one that has had all the blue molded capacitors or Allen-Bradley resistors replaced, but the transformers available today from Mercury will sound every bit as good or better than the originals, and as we have said so many times in the past,the Eminence Legend 15 is spectacular. Add some good,current production or NOS tubes and you will have been delivered to a place well beyond the common man’s limp and shriveled imagination. Now Quest forth….

Since getting up and rolling with a single amp model — the London — in 1004, 65Amps founders Dan Boul and Peter Stroud have been awash in creativity — and tone.
One of their newest models is the SoHo, which is configured as a head/cab and combo.
Like the rest of the company’s line they’re assembled using only high-quality components like low-tolerance NOS Allen Bradley carbon resistors in all tone-affecting positions, custom tone capacitors based on the original mustard cap, custom Mercury Magnetics transformers, ceramic power-tube sockets, Micalex preamp-tube sockets, sealed military-spec toggle switches, and matching valves from Groove Tubes. It’s all assembled on an aluminum chassis and meticulously placed in high-grade Baltic birch cabinet with 12″ Celestion speakers (one Alnico Blue and one ceramic-magnet G12H30 in the cab, single G12H30 in the combo).
Both rigs are dressed up with 65Amps’ two-tone Tolex and very retro “hot rod” dual four-slot heat vents trimmed in aluminum with gold piping, split-front speaker grill, cream-colored chicken head control knobs, and stitched leather handle; the overall look and vibe are definitely old-school and distinct — and instantly recognizable when you see, for instance, Peter Stroud playing them with Sherl Crow on CNN’s “Heroes” special, or with Rickie Sambora on “Saturday Night Live.”
Tube layout includes an EF86 (covered with heat-shrink and rubber O-ring to prevent “chatter”) and a pair of Groove Tubes 7025/12AX7 in the preamps, a matched pair of Groove Tubes EL84s in the power section (producing 20 watts) and a Groove Tubes EZ81 rectifier. The front control panel layout includes a pair of 1/4″ input jacks (high and low) a toggle switch to defeat/engage a master volume control, a six position “Bump” midrange tone switch, a Bump Level control, a Bump defeat/engage toggle, Bass and Treble tone stack controls and a Volume control, as well as Power and Standby toggle switches. Engaging the Bump circuit defeats the Bass and Treble tone stack and offers six midrange tone “bumps” that are controlled in intensity by the Bump Level control. The rear panel layout consists of a detachable AC power cord socket, primary and secondary fuse holders, a speaker output jack with an 8-16 ohm toggle, and a footswitch jack for the Bump feature.
Plugging a Fender-inspired Gadow Nashville with a Lindy Fralin single-coil into the SoHo head with the Bump circuit engaged and Master Volume turned off, the amp reveals a harmonically rich, dynamic clean tone with the mildly subdued mids, tight, punchy lows, and silky high-end response. The SoHo’s front-end creates a complex harmonic footprint — thick and in-your-face, no matter how lightly the guitar is picked or played, and ranging from sparkling clean to overdriven simply by modifying one’s playing attack. While most good tube amps “clean up” by simply rolling off the guitar’s Volume control, the SoHo takes it a step further by letting one’s fingers/pick do it, and without sacrificing the rig’s natural tone. The results were the same for each guitar we plugged into the SoHo, whether with humbuckers, P-90s or single coils — a solid tweed-flavored EL84 tone that didn’t steal any thunder from the guitar or its pickups. The Gadow’s tone pots required only slight tweaking (between the 10 o’clock to 2 o’clock positions) to compensate for different pickups. With the Bump circuit engaged, the SoHo’s overall flavor changes noticeably, jumping to a sweet British EL84 tone with more drive and pronounced, complex midrange. Each of the six Bump settings produces a subtle but very musical midrange boost. Again, each guitar/pickup combination sounds the way it should combination sounds the way it should — natural, with all overtones present no matter one’s picking style.
A feature missing here compared to many boutique amps is reverb, but the SoHo’s tone suffers not one bit given its complexity.
The Master Volume circuit serves two functions; it allows the player to pull back the overall volume of the amp (great for low-volume use), and it can be used to overdrive the preamp. Some degradation to the tone is apparent, but the guitar’s tone controls can be used to make up some of the ground. The fact that the Master Volume can be completely switched out of the circuit is a very nice feature. Though producing only 20 watts output, the SoHo gets plenty loud.
For the most part, the combo and the head/2×12″ cab setups perform the same, though the 2×12″ inherently offers more high-end snap and cone saturation compared to the combo’s 1×12″ setup.
The SoHo’s ability to cover a range of EL84 tones, from classic tweed to thick British, makes it very versatile. Throw in the switchable Master Volume and you’ve got an amp that will work great at a gig, in the studio, or in your den.
Source: https://mercurymagnetics.com/pages/news/VGmag/VGMar08-65amps.htm

Fender ’57 Amp at-a-Glance:
New look, classic tone
Handwired all-tube design
Limited run of only 300
Fender kicked the 5E3 Deluxe platform up a notch by using a Celestion Alnico Blue speaker in a new custom-designed maple cabinet with knurled ’57 logo knobs, solid aluminum handle and custom hardware. The amp includes a leather collector’s portfolio containing a certificate of authenticity, designer notes, factory photos and some other surprises. Custom-embroidered plush-lined cover included.
Limited run of only 300
Being a reissue of a classic Fender tube amp from the ’50s, the ’57 Amp was already certain to have an almost immediate cult following, but the fact that Fender is only building 300 of these beauties ensures that the ’57 Amp will be a hot commodity.
A revamped Fender ’57 tube amp chock full of tone!
The Fender ’57 Amp is a reissue of the revered Tweed Deluxe, an amp with the classic tone that helped propel Fender tube amps to top of the “most wanted” list of guitarists the world over. Each of these all-tube beauties is handwired and built within a solid maple cabinet with a black “piano lacquer” finish.
The ’57 Amp is built around a custom set of Mercury Magnetics transformers and loaded with a pair of 12AX7 preamp tubes and a matched set of 6V6 output tubes driving a 12″ Celestion Alnico Blue speaker. The ’57 Amp is handwired with all tube circuitry on an eyelet board with a late 1950s 5E3 circuit pumping out about 12 watts of true Fender tube tone. Tube tweakers and vintage enthusiasts can swap one of the 12AX7s for a 12AY7 to capture the lower-gain tone of the original Tweed Deluxe from the ’50s. Fender also thoughtfully incorporated a 5Y3 rectifier tube, which contributes to natural tube compression and “sag” when the amp is pushed harder. The ’57 Amp is a must have for Fender fans!

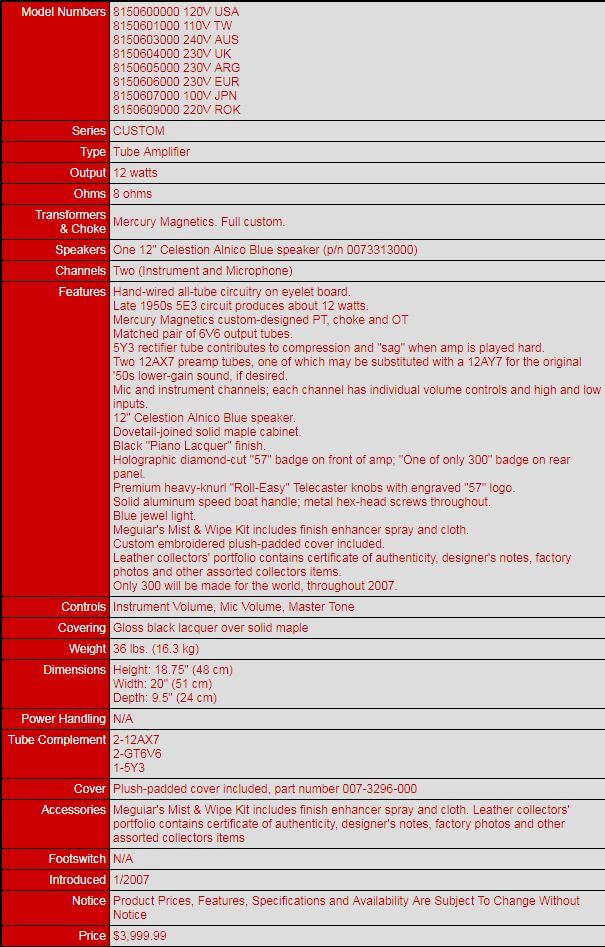
For more information, assistance, quotes or inquiries:
Source: https://mercurymagnetics.com/pages/news/misc/57Amp-Deluxe.htm

It only stands to reason that a guy whose day gig involves running his own successful and renowned pickup company knows killer tone when he hears it. So when the Jones hit to seek out a custom made map that combined the best of his favorite Blackface Vibroverb and Vibrolux, Lindy Franlin called upon Tony Albany and the guys at Vintage Vacuum Tube Amps to see if they might be up to the task. And that they were.
The holy grail would be to produce a 6L6 based 30 watt tone machine capable of a beautiful clean sound as well as a smooth, crunchy overdrive and be put captive into the smallest and lightest workable cabinet.
Beginning with a 2×10 Mojotone Tweed Super amp kit for the basic prototype, VVT and Fralin tweaked their hearts out for six months until they got it right.
Residing in a rather compact 20×20 cabinet, the VVT Lindy Fralin Model strikes a vintage pose in its white Tolex with oxblood-like grill cloth.
Beginning with a 2×10 Mojo tone Tweed Super amp kit for the basic prototype, VVT and Fralin tweaked their hearts out for six months until they got it right. Residing in a rather compact 20×20 cabinet, the VVT Lindy Fralin Model strikes a vintage pose in its white Tolex with oxblood-like grill cloth.
The VVT Lindy Fralin Model is a cathode biased straight forward, no bells and whistles affair. The “Plexi”top panel is simple and clean with its Input, bright switch, volume, treble and bass controls followed by the reverb control, standby and on/off switch. Chicken-headknobs let you know where you’re at. Two TAD matched 6L6 tubes supply the power with two 12AX7s for the preamp. A pair of 12AT7s are for the reverb driver and phase inverter. Rectifyin’ is courtesy of an Electro Harmonix 5U4GE. The cool thing is that the Lindy Fralin Model can also accept a deuce of 6V6s in place of the big bottles in the power section for a whole different vibe. Because of the higher plate voltages, VVT Amps stresses that only modern tubes (like the supplied JJ Electronics) should be used. You don’t want to blow the thing up, do ya?
If you think a 15 inch speaker might get as loose and floppy as your Auntie Mabel’s arse, you might be in fora pleasant surprise. With an obviously wider bass frequency range than a 12 inch, the Weber’sbottom remains tight and punchy with a nice lower mid section as well.Single coil and humbucker equipped instruments alike snuggled up quite admirably to the Weber Classic.
First impressions? The Lindy Fralin Model with my Strat spoke with gorgeous single coil chime and harmon-ic complexity, unabashedly magnified with a full trans-parent tone and organic beefy sustain. Very articulate and touch sensitive, the amp displays a more than impressive amount of projection. Both Lindy and Tony attribute this to the cross shaped members (called an integral diffuser) placed across the speaker opening in the baffle board which help disperse the sound and tame some of the“beamy” high end.
All tone controls are unobtrusive and very musical. While the treble is subtle up to around 6 on the dial, the bass is more evident from the get go but remains trans-parent throughout its range with no muddiness. The bright switch surrounds the notes and chards alike with an airiness without compromising the inherent full tone of the amp.
In addition to the Strat, the Lindy Fralin Model warmed up nicely to my other 6 string friends. The Carvin California Carved Top sounded sweet and detailed while my Ibanez AS200spoke with a very articulate, full and warm bodied tone.
Arch tops? This little box makes a nice jazz amp as well with clear, well defined chord structures and beefy single notes. With the fat axes pushing the volume past 3-1/2 caused a little mush in the low end which could probably be remedied by changing the first preamp tube to something with a bit less gain.
The reverb fills out the sound with a pleasant mix behind the dry signal. Throughout its range, the effect is very complimentary and doesn’t send your playing out to see even when dimed. For the dirty stuff, cranking the chicken head to the red(!) produced a bubbly, organic and throaty overdrive with real honest to goodness preamp/amp interaction. Very sweet with gobs of sustain. Doing a quick swap to the matched pair of 6V6s morphed the amp into a kind of Blackface Deluxe vibe with breakup noticeable at lower levels. The bottom felt a little less tight with a bit more perceived glassiness in the top end.
Whereas the 6L6 bottles speak “tux and bow tie” the6V6s are more “t-shirt and jeans”—not quite as complex but with a grittier and nice fat tone.
Also VVT Amps’ attention to detail gets a big thumbs up for the extra long line cord and groovy little spare fuse holder inside the back of the amp.
The collaboration between VVT Amps and Lindy Fralin has turned out to be a winning combination. The VVT Lindy Fralin Model’s beautiful, three-dimensional tones are equaled only by its straight-forward and no-nonsense design.
Tweed — 5E1 — 5 Henry, 370 Ω DC resistance, 40 mA current rating
2″ center to center mounting holes — same as Tweed Princeton choke
Tweed — #14684 — **Used in early Tweed amps w/ dual rectifier tubes
2.84 Henry, 400 mA current rating
Vertical mount — bolt hole spacing of 3 1/8″ center to center
Tweed — early ’50s
Early ’50s Tweed — 4, 8 & 16Ω taps — smaller size: Mounting Centers: 2-13/16″
Tweed Deluxe ’48-’52 era — 14k primary — 8Ω secondary #7766
Tweed — ’50s — 8k primary — single 4Ω secondary
Tweed Deluxe 5E3 amp — ’55-’60 era — #108 — 8 kΩ primary, single 8 ohm tap
Secondary has self leads like original — Horizontal frame — 3 1/8″ mounting centers
Tweed — single 2Ω tap. Uses Grain-Oriented Iron
Tweed 5E3 amp — #108 — Same as FTDO-59 with stranded leads (no self leads)
8 kΩ primary, single 8 ohm tap — Horizontal frame — 3 1/8″ mounting centers
Tweed — ’54. Uses Grain-Oriented Iron
Tweed — ’59 — Dual 8 Ohm taps (one optimized at 5K for use with two 6L6s the other optimized at 8K for use with two 6V6s). Uses Grain-Oriented Iron
Tweed — ’59 — Dual 4Ω taps (one optimized for at 5k for use with two 6L6s the other optimized at 8k for use with two 6V6s). Uses Grain-Oriented Iron
Tweed — 370-0-370 High voltage winding. Staggered gap, tuned core — #6452
Tweed (very early!) — special design — #6452
Tweed — stock B+ — 380-0-380 unloaded — #6452, amp models 5C3 to 5E3
Tweed — lowest B+ — 290-0-290 unloaded
Tweed — lower B+ — 335-0-335 unloaded
Tweed — lower B+ — 350-0-350 unloaded
Tweed — 388-0-388 High voltage winding. Staggered gap, tuned core — #6452
Tweed — medium-low B+ — 313-0-313 unloaded
Tweed — 220V, 230V & 240V primary
Tweed — Dual B windings: 260-0-260 and 310-0-310VAC — Single 120V primary — Not Available in Flat mount
Tweed — 100V & 120V primary
Tweed — 100V & 120V primary — Lower B+ — 335-0-335 unloaded
Tweed — lower B+ — 350-0-350 unloaded — Universal Voltage Primary
Tweed — lowest B+ — 290-0-290 unloaded — 220V, 230V & 240V primary taps
Tweed — lowest B+ — 290-0-290 unloaded — 100V, 120V, 220V, 230V & 240V primary taps
Tweed — FatStack — 100V, 120V, 220V, 230V & 240V primary — stock 380-0-380 unloaded B+
Tweed — lowest B+ — 330-0-330 unloaded — Universal Voltage Primary
Tweed — lowest B+ — 280-0-280 unloaded — vertical mount only — separate 64 volt bias winding
Tweed — Dual B windings: 260-0-260 and 310-0-310VAC unloaded — Universal Dual Primary — Not Available in Flat mount

I have always had a passion for music and audio. Guitar tone through an amplifier aroused my curiosity early on because many of the design rules for hi-fi equipment didn’t apply to producing great guitar tone. In the case of vacuum tube amplifiers, transformer design has a significant influence on the characteristics of tonality. Unfortunately, there is not a lot of reference material available and many of the original designers have either retired or passed away. In the early 1980s my partner and I purchased Mercury Magnetics, a transformer design and manufacturing company, from one of the early pioneers who founded this company in 1954. Our close proximity to the Los Angeles recording industry gave us access to studio technicians and many well-known musicians. Out of necessity, and to meet the demands of this level of clientele, we had to develop precise, “no compromise” methods of documentation and assembly techniques to rebuild and replicate these transformers to exacting specifications. A past example of this was when a legendary guitarist sought our services to help solve a frustrating problem. A technician had replaced the original output transformer in his amp with a generic copy, which resulted in completely changing the character of the amp. Several breakthrough albums from the late 1960s and early 1970s were recorded using this particular amplifier, and the sound of that amplifier really had helped define his signature tone. Needless to say, most musicians are very concerned about maintaining the character and unique tonality of their amplifiers. We ended up rebuilding his original output transformer and we provided two additional clones as backup.
TQR:Are you referring to all types of guitar amps, or more specifically British amps rather than, say, vintage Fenders?
I think that in all guitar amps, regardless of origin or brand, you also supplying custom transformers to amplifier manufacturers. Our extensive collection of vintage transformer designs really began to take off at that point in time. The ongoing accumulation of the finest sounding examples we could find inspired our line of ToneClone® transformers.
TQR: What is it about those particular transformers that make them so special, and how do you evaluate them? Do you install them in an amplifier and A/B them, or is it done more or less on paper?
We do have the necessary test equipment and software to check various parameters, but ultimately the ear has to make that decision. We also plug in, play, and conduct A/B testing at our facility. I have a dedicated sound room at home that has been tuned for the purpose of testing and evaluating audio equipment. We are lucky, because the Los Angeles area offers us an amazing amount of guitar playing talent that continues to help us maintain a level of objectivity. Also, some of our best listeners are avid tone enthusiasts who work in and for the local studios. These people understand good tone and give us their experienced opinions.
TQR:And can you describe what it is that makes these transformers special? What would we hear, specifically?
Having a detailed transformer spec is only the beginning. Breaking down into fine details what materials and assembly techniques were used decades ago helps us assure our customers an accurate reproduction of vintage tone. We have carefully selected the best of new and old technology to put performance and quality ahead of economy. Our transformers are hand-wound and the cores are hand stacked. Some materials we fabricate in house, and others, like our steel laminations, are custom ordered. Because we build them one at a time, the Axiom and ToneClone series are only available in limited quantities. Consequently, there is an audible difference between a budget transformer and an Axiom or ToneClone.
TQR:Can you describe the audible differences?
A good output transformer should go beyond its job of impedance matching, and an amplifier’s overall personality depends on it. A desirable output transformer’s distortion has more detail. The harmonics seem even and smooth. Played clean, the transformer should sound natural without harshness, obviously within the boundaries of the authentic tone characteristic the player is eeking. Better said, we still can’t make an apple into an orange.
TQR: What are some of the comments that you hear from players when they hear the Axiom or ToneClone transformers that you build? Is it a matter of touch dynamics, harmonics, all of that?
Yes, and let’s not forget musicians’ colorful tone speak, such as: The amplifier sounds more open, glassy, sweet, brown, fat, with more notes perceived. Barred chords are not muddy or squashed. Chimes and bell tones are much more apparent. Good note separation, sustain improved, more definition, etc…
TQR:And these things can all be affected by the output transformer in some considerable detail….
It is pretty much the last tone filter in a series of components. Other factors like tube quality and speakers can play an important roll as well. Also, if you were to look at an amplifier circuit as a modulated power supply, then the quality of a power transformer and choke, if a choke is used in the circuit, also affects tonality. The ghost note phenomenon would be an example.
TQR:Like a few amplifier builders we know, you have taken the direct route of precisely replicating the materials and tolerances that comprised the industry standard decades ago…
I remember having a conversation with Leo Fender a number of years ago and getting a chuckle out of him as he told me how amazed he was that so much scrutiny was being given to how things were done in the early days of Fender. He said that they had taken what they were doing in the ’50s and ’60s so matter of fact back then. They were hardly thinking at the time that they were building future classics. They were trying to make an affordable, good sounding, quality amplifier while still trying to make a buck. Leo also mentioned that for reasons of cash flow and/or inventory problems, they would resort to using alternate vendors from time to time. They kept a careful eye on cost of materials, and their supply, rather than hand picking components with alleged magical tonal qualities.
TQR:They weren’t matching tubes, either. All of this can and does get out of hand, but when your rig sounds so good that you can get lost in the magic of it, as a player, wonderful doors can be opened.
Years of research led us to the conclusion that not every aspect of a vintage transformer needed to be copied. There were problems and limitations in their day, so why repeat them? We achieved better results by combining old and new technologies. Making the math work for the best tone characteristics together with improved consistency and longevity is the formula we chose to follow. There are a lot of vintage amps today with transformers that are going bad simply because they have aged. The tonal quality of the amp is deteriorating along with the transformer. Paper and certain types of varnishes used in these transformers tend to have hygroscopic properties. Moisture is absorbed over time, affecting the insulation system and increasing the chance for high voltage breakdowns. To make matters worse, the primary winding voltage is high enough to produce a corona effect whose ions help oxidize this insulation. Over time, reliability and tonality will suffer. Do you believe in transformer cancer?
TQR:That leads us to an interesting situation in which the original output transformer in our ’60s Pro Reverb died, and we noticed how much better the amp sounded when we had installed a new transformer, which was a commonly available unit sold by MojoTone. Now, the amp sounded great before the old transformer went out, but it sounded significantly better with the new transformer. I asked our tech and advisory board member Jeff Bakos if it was possible for an output transformer to gradually decay over time, dying a slow death while you continue to lose ‘tone’ in a very subtle fashion over years of use. Is that possible? It seems as if that was the case with our amp, which we had always considered to have a rather legendary vibe.
Not only is it possible, it is probable. Keep in mind that if high voltage insulation breakdown has started, there is no reversing it. Assuming that the transformers insulation system is intact, we have in the past reversed some tonal degradation in original transformers under controlled laboratory conditions. I’ve proven that point with my more cynical, high-end customers. One example of this is an amp (a Marshall JTM 45 or a Plexi – I forget which) that had been used in England for years and then brought over to the United States. The owner felt that the tone had decayed over time, seeming darker, lifeless, and the higher frequencies were less pronounced. We asked him to remove the transformer and all we did when he brought it in was to re-bake it in an oven to drive out the moisture. We then vacuum impregnated the transformer with our proprietary resin to hermetically seal it before the final bake. He put the transformer back into the amp and the results were pretty amazing… it became a lot brighter and more detailed from the upper midrange to the upper frequencies. I’m not recommending that anyone start baking their old transformers, however….
TQR: No, but it seems to be a fair statement to say that it’s possible that your good sounding old amp might sound significantly better with a new output transformer. At least that was our experience, and in hindsight, we didn’t realize what we had been missing.
That’s true. The tonal degradation I’m speaking about is very slow and gradual. Your results would be even better if you had used ToneClone transformers. Any of our transformers should outlast older vintage transformers because each are put through the same process during production.
TQR:Doesn’t it become particularly more problematic with amps like AC30s and Hiwatts, where repro transformers have typically been poor compromises at best?
I believe that Marshall, Vox and Fender, to name a few, are doing an outstanding job of building affordable vintage reissue amplifiers. When an owner of one of these fine amps wants to take his/her tone to the next level, they will usually consult someone like a Don Butler (Toneman) for example. Don is an expert in the field of amplifier upgrades and the art of tonal improvement. Don is also one of the key figures in this mini industry, which is similar to the aftermarket for automobiles and motorcycles. Much like an engine tuner, Don will replace transformers and other components in the signal path to give the customer an upgraded, outstanding sounding amp that comes much closer to capturing the original tone they were seeking.
TQR:Your website seems to be very comprehensive, but can you be contacted over the telephone for customers that either don’t see their amp listed or perhaps have additional questions?
Yes! Paul Patronete, an accomplished guitarist who has a good ear for vintage tone and heads our MI division, is happy to help those customers when I am unavailable. Our website is constantly being updated with vintage and modern transformer versions. We will probably always be two or three pages short of having all of the various models listed that people may be interested in. Of course, we can’t possibly list every one-off we’ve done. Another cool thing we offer are modern, updated versions of many of the classic transformers. We have added output impedance taps for many of the classic Fender transformers, which were never originally offered. For any make of amplifier, we offer various mounting styles from the original. We can, in addition, alter tonal characteristics to fit the unique needs of each customer.
TQR:Are you building transformers for many small builders?
Yes. If you own a high end, small production amplifier, there is a chance you will find a Mercury Magnetics label on the transformers. Some exceptions are when certain amplifier manufacturers remove labels in an effort to keep us and other vendors a secret. We do maintain a confidentiality agreement with all of our customers if this is their desire.
TQR:Schumacher was a primary supplier to Fender during the tweed era, and they are still operating, although we understand that you generally have to be capable of placing a fairly large order to get geared up. That seems to be a significant barrier to many would-be amp builders.
That company is doing a good job of supplying inexpensive transformers to a high volume market. When a lot of emphasis is placed on meeting price points, something has to give. The cost of labor and materials are logically their first consideration. The end result is a compromise, and who could blame them? Ultimately, end users will determine if the resulting tone is adequate. Someone who has paid several thousand dollars of their hard earned money for a “high end” amp is expecting to have something that excites their senses along with a build quality that justifies their investment. This is where we can assist the amp builder. It goes beyond Mercury Magnetics “sending in the clones.” We have made every effort to break those barriers by eliminating minimum buy requirements. We work closely with today’s designers and builders to provide them with a thoughtful, next-level approach to their signature tonal requirements.

The en vogue status of low-wattage combo amps remains a boon for any guitarist on the lookout for a compact amp. Just about every major amp company and most boutique shops are offering at least one model in the 12- to 18-watt range and that’s a great thing. What’s not to like about an amp that you can push hard without blowing out the windows or that you can throw in the front seat of your car for a gig?
Nolatone Ampworks — and the work of Paul Sanders — are already standouts in this fast-growing amp category. Hand built by Paul in Raleigh, North Carolina, using only the highest quality parts, Nolatone models like the June Bug and Chimey Limey have already made a mark for their interpretations of Fender Tweed and Vox tones. They might also be some of the sharpest looking amplifiers available today. And on both the sound and visual front, Nolatone’s 15-watt Rotten Johnny is every bit as spectacular a performer as its cousins in the Nolatone line.
The Dirt
Weighing in at a very reasonable 28 pounds with dimensions similar to a Fender Blues Junior (18″ x 16″ x 10.5″), the Rotten Johnny is an open-back 1×12 combo constructed of solid dovetail-jointed pine. Our review Rotten Johnny came in covered in two-tone brown and crème vinyl with basket weave grille cloth, and sported the signature Nolatone “V” panel TV front design. The 12″ speaker is a 25-watt Warehouse Green Beret, which is designed to sound like a broken-in Celestion greenback. The circuit is built around two JJ 6V6 power tubes (you can also request EL84s) and two 12AX7s. Everything under the hood is top-notch, including custom Mercury Magnetics iron, 1-watt carbon film resistors, F&T filter caps, Switchcraft jacks, and Carling switches laid out on a hand-wired turret board.
Unlike many lower-wattage amps, the Rotten Johnny offers far more control options than a single volume and tone control. The top panel consists of a unique 3-band EQ (Bottom, Mid, Top), as well as Pre- and Post-Gain controls and a Master volume. A Mid Lift switch (which can also be activated by a footswitch) effectively works as a boost for solos. Power and standby switches reside next to a red jewel power indicator.
The EQ section is a little more flexible than what you’ll find on a production-line low-watt amp. The Bottom control is a 6-way switch that progressively rolls off bass. The independent Mid control is not part of a typical tone stack configuration — dialing it down extends the highs and lows to create a very Fender-like mid-scooped tone. The High control, meanwhile, is a Vox-style top-boost reverse-wired to enable players to move from chiming to much darker tones by backing off the control. Borrowing a move from Nolatone’s June Bug design, the Pre- and Post-Gain controls work in tandem to control the amount of gain to the second stage and phase inverter respectively.
Rockin’ the Filament
With a Godin Icon Type 2 with Duncan P-Rails in hand, I got right down to the business of exploring the wide-open voice of the Rotten Johnny. With the Godin set to the humbucker position, I cranked the Master to full, set the Post Gain to around noon and brought up the Pre Gain until I got a rich, full distortion. The sound was raw and thick, but I wanted a little more clarity, so I dialed back the Bottom knob by a few clicks, scaling down the thickness a touch, but opening up the sound considerably. The combination was reminiscent of Frampton’s Rockin’ the Fillmore-era Humble Pie tone — a pretty huge sound for a 15-watt 1×12 combo. And if I closed my eyes, I’d swear I was listening to a full stack in miniature. For years, I’ve tried to harness 100- and 50-watt amps with attenuators and master volumes and never been totally successful. Needless to say, I was stunned when two 6V6s pushing a single 12″ gave me what I’ve been looking for—and then some.
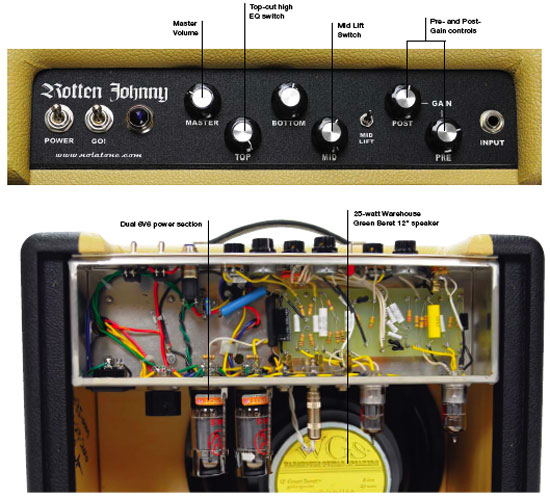

Wielding my ’74 Les Paul Custom and with the Mid control set to the non-lift position, I was able to dial in AC/DC rhythm tones with just the right amount of kerrang and chime to create the illusion of a blaring baby JTM45. And setting the Pre Gain to noon and ramping up the Post Gain added gobs of thick, juicy crunch with just enough bark to cut through a mix. This is where the Top control really shines — pulling the Top back just a touch takes some of the edge off without muddying the tone. It’s voiced for just the right amount of sheen and clarity without ever being brittle or ice-picky. The top-cut configuration also makes the effectiveness of the Mid control’s sweep range very apparent — enabling boosts in presence that aren’t too brittle.
The Mid control is almost like another gain knob, delivering more distortion and dimension the more you crank it. And with the Mid Lift engaged Rotten Johnny turns into a roaring fire-breather with more gain than most of us would ever need. I’ve rarely heard a 6V6 amp sound this way — often assuming some of the tonal qualities of EL34s and EL84s. Though it only takes cutting the Mid and backing off the Pre Gain to get back to more blackface-like territory that was a perfect match for my Strat.
For a 15-watt amp, the Rotten Johnny doesn’t lack headroom. Because there is so much control via Pre and Post gain over how hard you hit the tubes, I found myself digging deep into the wealth of Strat-friendly clean sounds you can get with less aggressive use of those controls. It was easy to conjure thick and chewy cleans with just a hint of grind by pushing the Post Gain and leaving the Master wide open. Even with the Mid Lift engaged I could still hit the guitar hard without harsh sounding breakup. And I was always able to shape the thickness with the Bottom switch, which I used extensively to match individual guitars to the amp.
The Verdict
It’s been a long time since I’ve been so excited about a new amp. The Rotten Johnny has a huge range of brilliant tones in a compact design that, at $1399, doesn’t break the bank. For bedroom or studio musicians, it’s a dream because you can coax out cranked stack sounds without knocking down walls and get the most beautiful cleans with the twist of a few knobs. The construction is top notch and the styling is classy and cool. For an amp that’s roughly the same size as a 1×12 cab and weighs less than 30 pounds, it has the sonic personality of something much larger. I only wish this little guy was around when I first started playing guitar. Thankfully, I’ll have the chance to make up for lost time — my own Rotten Johnny is on the way and I can’t wait to cut loose.
Buy if…
you want everything from Brit aggressiveness to blackface tones in a compact package at a fair price.
Skip if…
you actually need the power to blow down barns.
Rating…
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Source: https://mercurymagnetics.com/pages/news/PremierGuitar/PremierG-30.htm

Many of you are already familiar with our resident amp tech, studio owner/engineer and advisory board member Jeff Bakos. In his spare time, Jeff occasionally builds amps for clients on request, and lately he’s been asked to build… you guessed it – small little biters. Since his personal GA-5 has been featured so often on various recording projects, Jeff toyed with the idea of recreating the Gibson GA-5 Skylark for a minute, but given the fact that vintage GA-5s remain fairly plentiful, he ultimately decided to design his own simple take on a smallish amp – the 8 Ball. Housed in a Mojo Champ cabinet, the 8 Ball is built with one of our favorite tens, the Eminence Legend Alnico 1058 (that’s a hint), Mercury Magnetics trannies and choke, and premium components, including Sozo coupling caps. With the bigger Mercury Princeton transformer set, the single 6V6 / 12AX7 / 5Y3 design is capable of producing 10 watts of power. Features include dual inputs, volume and tone controls, a front panel line out jack, and a “vintage” / ”modern” toggle switch also conveniently mounted on the front panel.
The “vintage” setting produces pristine Fendery clean tones up to 12 o’clock on the volume control, gradually followed by a progressively thicker growl with intense distortion and sustain. In this setting, the 8 Ball surpasses all the other small amps we’ve reviewed in terms of practical versatility with stronger, louder clean tones and a more gradual It’s back! We are now resuming limited production of our meticulous recreation of the original 1959 DeArmond R15 1×12 amp. You may recall that we initially produced a limited number of TQ Clarksdale amps in 2006, before our supplier for the original chassis informed us that small runs would no longer be possible. We’ve found a new supplier, and the TQ Clarksdale “DeArmonds” will be built again by Jeff Bakos with our original specs – pin cabinet construction and design identical to the original, original Mercury Magnetics Tone Clone transformer set cloned from our original ’59 DeArmond, hand-wired chassis, premium components including Sozo caps, Celestion G12H 70th Anniversary speaker, premium JJ and Tung-Sol tubes, Evidence Audio speaker cable, custom gold grill cloth and blonde Tolex covering. This 22 watt design represents one of the rarest and most toneful combos ever built. The original 1959 DeArmond 1x12s were built for just one year in Toledo, OH, and a clean example recently sold on eBay for $7000. In 2006 Jeff Bakos meticulously blue-printed our original DeArmond, Mojo created CAD drawings from the original cabinet design, and we sent the transformers to Mercury Magnetics to be cloned. The result is a phenomenal 1×12 that will generally kick any tweed Deluxe straight to the curb with a bigger, bolder voice and lush, musical distortion cranked. The 4-input, cathode-biased Clarksdale can be operated with dual 6V6s and 5Y3 rectifier for optimum burn, or a pair of 6L6s and 5AR4 for slightly more power and clean headroom. Blonde Tolex only, simply because it’s the coolest color…

You want amps? You had ’em at the 2009 NY Amp Show! Loni Specter ran another trouble free amp extravaganza at the Embassy Suites Hotel in Piscataway, New Jersey. There were approximately 64 exhibitors showing their stuff to hundreds of guitar players in attendance. So many goodies, so little time. All right let’s get down to who we had the pleasure to meet and sample some of their creations.
Now with my head spinning a little from checking out all this cool gear a small pile of daphne blue Tolex amps caught my eye. This was the Nolatone suite. Paul Sanders is the builder and designer of the Nolatone amps. He brought along the Chimey Limey (can you say fat AC15?) that has a switch on the back of the chassis to select either a 12AX7 or EF86 for the first gain stage. The 5 watt June Bug which has 3 gain stages for thick sounding overdrive and a removable baffle ring to accommodate a 10″ or 12″ speaker. And last was my personal fave the 22 Tango. This was one of the loudest, clearest 2x6V6 amps I ever heard. It reminded me of a tweed Bassman tone with tone stack controls that were much more effective. Paul says that the big, clear sound has to do with the special Mercury Magnetics RSO-type output transformer. Whatever the recipe is it sounded great and had a big amp feel to it.

Ten years after our first published amp review (the blackface Vibrolux Reverb), we still find ourselves answering readers’ questions about which amp to buy. We’re not complaining… your subscription to TQR has always included phone or email access for those contemplating a new gear purchase, but it seems that published reviews can still sometimes prompt more questions than answers. We understand, and like you, we are routinely faced with these same buying decisions just about every month as we look ahead to future issues. “Power” and “headroom” (or lack of it) seem to remain among the most daunting considerations for prospective amp buyers. This may not keep you up at night if you’re looking for a toneful box to play solely at home, but the range of clean and overdriven tones available from a single amplifier that can hang with a band is absolutely critical – the tipping point for guitarists who wish to have both clean and grittier tones available on the fly. And even the casual “bedroom” player (does anyone really play their guitars in the bedroom?) will quickly discover that big, lush guitar tones – clean or jacked into rich distortion – are often best obtained through a “bigger” amp. We’re not suggesting that we don’t love our ’58 tweed Tremolux or ’64 Deluxe – they both uniquely, timelessly epitomize great guitar tones – but an entirely different realm exists within the range of vintage Fender amps, and try as we might, we have never found another amplifier quite as versatile, user-friendly or uniquely toneful as the blackface (1965–7) 40 watt Pro Reverb – still the most under-valued and overlooked reverb amp from the entire blackface era, although aside from its 2×12 speaker configuration, the Pro is nearly identical to the Vibrolux and the Super Reverb amps.
Yes, the 2×12 Pro Reverb can move some air, just as an AC30or Matchless DC30, both highly coveted amps for good reason, do the same. Experienced in a room, 2×12 amps produce an ambient presence and a spatial quality that single 12s can’t match. That extra speaker isn’t adding volume as much as it simply disperse sound effectively by filling more space. And although the Pro Reverb is rated at 40 watts, the smaller output transformer Leo Fender chose to use delivers only 28 watts, probably in an effort to minimize speaker failure, yet the original Oxford and Jensen 12 s shipped in the Pro still blew when pushed by enthusiastic rockers. A well-maintained Pro Reverb will typically produce classically clean Fender tones with strong bass and treble and slightly diminished mids from “2” on the volume control to “5,” gradually spilling into lush Fendery distortion at higher settings. If you choose to use an overdrive device to achieve distortion at lower volume levels, the Pro will sound significantly better than most 20 watt amps because your pedal is affecting a cleaner signal, rather than adding distortion to an amp already spilling over into distortion. And as we have reported so often in the past, non-invasive and completely reversible modifications can be made, such as the addition of a 25K mid range pot utilizing the existing back panel hole for the extension speaker jack. This single mod enables the Pro to develop a very ballsy British voice as midrange is increased, while completely preserving the integrity of the original Fullerton tone with the midrange pot set at zero, rendering two outstanding amps in one. Intrigued? You should be, because we have never heard a contemporary boutique 2×12 combo amp that can approach the sound of a Pro Reverb equipped with a solid set of tubes and speakers. And with the range of speaker options available today, you can effectively custom design and shape the sound of your Pro for more of a traditional, bright“American” sound, a heavier or chimier British tone, or the two combined.
Ah, but buying old amps is risky business says you… what if I get a “dog” or it needs a lot of work? I’d rather buy some-thing new and not deal with the unknown. Fine, do that. But for those willing to reap the rewards that only a certain degree of risk can offer, it’s not that difficult to minimize your chances for disappointment. Here’s how:

While Michael Bloomfield was playing cranked up blonde Fender Bassman and blackface Twin Reverb amplifiers, Marshall 100 watt stacks suddently appeared thanks to The Who, Jimi Hendrix, Cream and Led Zepplin. Throughout the ’70s, rock was dominated by the sound of a Les Paul and Marshall amps, but despite its reputation as the ultimate rock machine, all four-input, 100 watt Marshall model “1959” heads are not the same….
The first 100 watt Marshall amps appeared in late 1965,and despite Marshall’s decision to drop tube rectifiers for the less forgiving, harder sound of solid state diode rectification, the “Plexi” 100 watt heads remained more closely related to earlier Marshall amps inspired by the tweed Bassman than the Super Leads that would follow. In the early ’70s, the 50 watt model “1987” head and 100 watt Super Lead were gradually modified to produce more gain faster, and the bright channel was pushed to a punishing level of thin, ear-shattering brightness, while Channel II remained too dull and bassy to be used alone.
We acquired a 1973 Super lead—the last year before Marshall switched to printed circuit boards—for the modest sum of $1,000, made possible by a recent Dagnall replacement output transformer. Two .022 mf caps had been replaced with Orange Drops and another removed altogether in a futile effort to reduce brightness and gain—other-wise, the original Super Lead circuit remained intact and unmolested. Our plan was to run the amp at approximately 60 watts with just two EL34s, requiring the amp to be set at half the rated speaker impedance of our 8 ohm 4×12 Avatar cabinet, loaded with two Celestion Gold Alnico 12s and two “Hellatone” 70th Anniversary G12H 30s.
As we discussed this project with Jeff Bakos, he mentioned that the 100 watt Super Leads not only sound very different from the 50 watt heads in ways that transcend a mere increase in power, but he also felt that the 100 watt Super Lead amps sound better with just two powertubes instead of the full compliment of four…“That’s very common down here—I know a lot of layers who prefer that sound.” We also consulted with Sergio Hamernik of Mercury Magnetics on a suitable replacement for the modern Dagnall OT, and he suggested the ToneClone’69 Marshall self-leaded version. “Self-leaded” means that the actual wires wound within the transformer are extended to connect directly to the amp, rather than smaller diameter lead wires being attached to the transformer internally. Installing a self-leaded version is a bit of a bitch, since you are cutting and bending much heavier gauge wire to fit in tight spaces, and the insulation must be scraped off the wires before soldering. But Jeff had been here before,and all was taken in stride.
We also noted that the original power transformer in our ’73 Super Lead was similar to those found in the early Plexi100 watt amps with plate voltages well above 500 volts.
Our amp measured 522 volts, while the plate voltage on most post-plexi 100 watt “1959” amps are usually lower—around 460 volts. The “hotter” transformer in our Super Lead produces a comparatively higher and less compressed distortion threshold, and if not for our pair of NOS MullardEL34s, we might need to be more selective about choosing current production tubes that can withstand +500 volts on the plates. Jeff was confident that JJs would hold up, less confident of Svetlanas.
We took the Marshall home and initially ran it with three spare Telefunken 12AX7s just to see if they sounded as sterile in a guitar as we had recalled in the past. They do. We could hear a distinct improvement in the mid and bass tones with the new transformer, but the bright channel remained far too bright to be used alone, even with a Les Paul. While we could manage to knock down some of the treble and acquire a decent tone with the bright channel set on “3” and the bass channel patch with the volume on “6,”pushing Channel II so far above the level of bright channel introduced an indistinct woofiness we didn’t care for. The next day we returned to Jeff’s shop for his standard Marshall 4-banger input channel mod, which simply involves moving the original .005 mf bright cap on the bright channel to the basier Channel II. We had done this before with our ’69 50 watt and a vintage PA20, and it unerringly transformers the sound of the notoriously dull Channel II to a fat, warm, musically rich and bright sound that works perfectly every time. We also replaced the two Orange Drop caps with Mallory 150s and pulled the super hi-fi Telefunkens, replacing them with NOS RCA 12AX7s—the warmest, creamiest pre-amp tube ever made.
With the Super Lead thus optimized and tweaked, its voice was transformed from an angry soprano chain saw to a classic Marshall with all of the requiste thick,rich, historic hall of fame tones at our fingertips. We could mine brilliant clean tones on “3” at a usable volume level that revealed all the gorgeous detail of the vintage patent number pickups in our Historic Les Pauls, and our Stratocaster, Nocaster and Les Paul Junior all sounded equally good. Add Fender outboard reverb and you do indeed have the Twin from Bloody Hell.As Jeff predicted, the big power supply in the Super Lead also produced a much more formidable and impressive presence than a typical 50W. Yes, the Super Lead is still a beast, tamed for your consideration and our enjoyment. But if classic Marshall tone is the sound you crave, a properly groomed Super Lead is hard to beat, and given today’s boteek and vintage amp prices, it’s a solid steal.

You plug your prized mint-condition ’51 Fender Deluxe into the wall socket and crank it up. Next thing you know, you’re blown the transformer, the caps have puked, or you’ve toasted an original speaker. And you think to yourself, “Okay, the amp is 50 years old. It was bound to go sooner or later.” But maybe it wasn’t… an maybe age had nothing to do with it.
If you plug a vintage amplifier directly into a wall socket, chances are you’re not hearing what that amp sounded like back in the day. And that’s not because the amp is old and worn out; most old amps will run forever and sound great if treated well and maintained. But they don’t, because while that old amp may have sat in a closet for 50 years untouched, something else has changed over time — wall voltages.
Amplifiers from the 1940s, ’50s and ’60s were meant to run on 110 to 115 volts AC, while amps made in the ’70s are mostly rated at 117 volts. The back of an amp should indicate the wall voltage for which the amp is designed. The closer to new an amp is, the higher its optimal operating voltage. Depending on where you live, wall voltages fluctuate on a daily basis, and range from 100 to 130 volts! And that’s not taking into account the daily spies in power experienced on almost every line — power surges, transient voltage spikes, and of course that weird static sound that comes out of your amp, or the occasional radio station.
So, what does an extra 20 volts mean to a vintage amp? More bone-crushing power? More whump? Or is it a recipe for disaster? And is there anything you can do about that nasty static that sounds like you’re playing in Dr. Frankenstein’s lab?
Roy Blankenship, founder and president of Blankenship Amplification, recently sat down to offer some answers. Blankenship has worked as an amp repairman, production manager at Groove Tubes, and more recently — at the prodding of incessant customers — he began building a line of amplifiers. Today, he is one of the preeminent boutique builders (his Leeds 21 was one of the amps scrutinized in VG’s “5×18 = British Crunch Bliss” feature, December ’07).
* * *
VG: Is there a risk plugging a vintage amp meant to run on 110 volts into today’s standard 125- to 130-volt all current?
RB: Yes and no. Your power transformer doesn’t really care all that much, because all it’s doing is taking the voltage coming in and creating secondary voltages to send out. You’re probably not going to blow it by loading it with 20 to 30 more volts than it was rated for, depending on how much current is being drawn on the other side of it. Fortunately, most amps, like Fenders, had enough reserve built in that you will not be exceeding their specifications.
The problem is with an amp’s capacitors and filament voltages. The caps were rated for a certain value, usually about 450 volts. Most amps use 500-volt capacitors, so if you’ve got an old amp with original caps, you risk over-voltaging them. The collectors with pristine, all-original amps aren’t playing them, anyway. They sit in a closet or a glass case.
An amp’s electrolytics were designed for a shelf life of 15 to 20 years. So if you want to play your old amp — and you want it to sound good and not endanger your trannies — you need a cap job. Once you put new 500-volt caps in it, you’re going to be okay.
Some boutique makers now are doing what they call “voltage correction,” utilizing components so the amp will run at the original voltages. A certain percentage of my clients are concerned with authenticity, and this follows that vein.
The other thing you can do is just run the amp down a bit on a variac, which can accomplish a couple of things; it provides a safety margin, and lets the amp produce tube saturation at a lower volume.
VG: A lot of guys are using variacs to control output power, and your Variplex has one built in. Why the sudden boom?
RB: One of the original uses of a variac was as a diagnostic tool. When an amplifier is repaired, you turn it on using the variac starting at 0 volts. As you increase the voltage, the current draw on the “Amperes” meter (or ammeter) on the variac lets you know if there is a short within the amplifiers. On a tube amp with a tube rectifier, it’ll give an indication of current draw relating to the bias/voltage relationship. If your ammeter is slowly going through the roof, you have a bias problem. If you advance from 0 volts and the ammeter pegs itself, you have a shorted tranny, capacitor or power tube.
When Edward Van Halen came on the scene, he spoke of using a variac to alter his sound. Everyone wanted to sound like Eddie, so the variac became a fixture in a lot of people’s minds. While he initially claimed he increased the voltage on his amps, it was soon discovered he actually dropped the voltage to get his “brown” sound. Because musicians are so impressionable, I think it was a really bad idea to say this, because cranking an amp up to 140 volts can distress components to potential failure. As this information evolved, however, a lot of guys were discovering they could use the variac to reduce the line voltage, which causes an amp to break up sooner while otherwise retaining its sound.
Everybody knows that with tube amps, you’ve got to crank them to make them sound like they should. The sound of a guitar plugged straight into a naturally cranked up amp cannot be duplicated with a pedal. The variac allows you to get that same overdrive — that same touch sensitivity you get when the amp is dimed, but at a lower power level.
My friend, Bobby Carlos, who is a tech for Don Henley, uses a variac for small venues and says the amps sound fine down to 80 to 85 volts, then they lose integrity. When he was playing one of my amps with a Mercury tranny, he was down to 70 volts and it was hanging in there, illustrating that the quality of the transformer is also a consideration.
VG: Can a variac damage an amp if it’s running it at lower power?
RB: That’s a widely held belief, and one of those issues that does not have a simple answer. The problem is with the tubes, which were designed to operate on a 6.3-volt filament voltage. You can drop it some, but when you get too low, electron flow is disrupted; tubes work because of electron flow. So when you get below 80 or 85 volts, the amp sounds like crap. so that’s about as far adown as you can go in most situations.
Now, when you use a really robust transformer, you can take the amp down further. Mercury transformers make my amps work, in particular the Variplex, which stabilizes the filament voltage and varies the bias and the B+. Mercury trannies track perfectly as the variac is turned down — the sine wave on the oscilloscope does not change in character as you go from 60 watts to five watts.
I know people who’ve been using variacs for years and they’re still running the same tubers in their amps, and they still sound fine. My opinion is that you’re potentially going to have problems running the tubes down below 6.3 volts, but in the final analysis, when a preamp tube lasts 10,000 hours, if you get a sound that turns you on and makes you play, who cares if you have to replace a tube every 10,000 hours or so?
Some guys like running regulated filament supplies to make sure tube voltage stays at 6.3 volts, because that’s what the tube wants to see. Certain tubes may react differently to changes in the filament voltage.
VG: Will a variac work with every type of tube amp?
RB: It will, but the results will vary from amp to amp.
| Actual voltage | B+ | Filament | Screen | Plate | Current Draw |
| 110v | 356 | 6.05 | 292 | 345 | 34 ma |
| 125v | 406 | 6.88 | 331 | 392 | 39 ma |
| The increase of 15 volts in the AC line causes significant voltage increases in the amp. The caps in this amp were rated high enough that there was no distress, but a lot of amps are close to the ratings at 110 volts, and would be endangered by running at 125 volts. The B+ is the main operating voltage coming off the rectifier tube (which converts the AC from the power tranny to DC). The current draw is a milliamp parameter off the cathode of the tube an is what is measured when people talk about “biasing” their amplifier. This being a cathode-biased amp, the number is higher than in a fixed-bias amp. | |||||
VG: What’s the best type of variac?
RB: Well, a variac is just a voltage regulator. It’s not a precision device. All it does is regulate the voltage from the wall to the amp’s power transformer. A decent one will probably run $50 to $75. Even the Chinese ones are reliable as long as you don’t drop them. What’s more important is that you have a good-quality multimeter, which is invaluable for maintaining gear and diagnosing problems. If you want to use a variac, it’s important to measure the actual output. Just because a variac says “110 volts” doesn’t mean that’s what is coming out. In my shop, it varies 5 to7 volts from what is indicated, sometimes dependent on the time of day. I did some measurements in a ’51 tweed Deluxe to give an idea of the differences between 110 volts and what comes out of the wall these days (see chart).
VG: What the “brown sound” the premise of the Variplex?
RB: We wanted to create a great-sounding amp that you could turn down to about 5 watts, so when you play a big room you have the power, but when you play a little room you’re not killing people in the first three rows. Really, we were trying to get a great Plexi Marshall sound, not a Van Halen sound.
Now, there are other ways to achieve distortion at lower volumes. Attenuators have become popular for achieving a cranked-up sound, as have master volumes and a process called “power scaling” invented by Kevin O’Connor. We liked the sound using the variac and chose that process. A master volume smashes your preamp tubes into square waves, but the power section really isn’t working. The great appeal of the variac is that the whole amp is balls-out no matter what volume it’s running. It sounds like a cranked amp, not an effect.
VG: What about all those awful static electricity sounds, especially with older amps that don’t have grounded cords, And also, radio signals. Is there any way to get rid of them?
RB: There are numerous devices that will get rid of what’s called electromagnetic interference (EMI), and radio frequency interference (RFI). These include ETA Systems, Furman, ART, Juice Goose, Tripplite, Atlas, etc. These companies specialize in products that “clean” electrical current. And there are some amplifiers that have an EMI/RFI filter in the AC input. And remember the old Acoustic 270? It had a little resistor/capacitor network on the output as an RF filter. Any of those I’ve seen that have been in some kind of city environment have burned out from too much “dirty” electricity.
A lot of times, radio signals through your amp means you have a grounding issue in the input section. It needs a ferrite core or a .1 capacitor to the chassis at the input jack. A lot of houses, especially older ones, will get rewired with three-prong plugs in the wall sockets, but they’re not grounded. There’s a circuit tester that tells you what’s going on just by plugging into the wall. They let you know if polarity is reversed, whether there’s a ground, etc. Sometimes, this can be a lifesaver. I know guys who have played clubs where one of these tools has saved them a lot of grief because they found out the club owner allowed the bouncer to come in and rewire the place. They would have gotten the shock of their lives if they’d plugged in and played.
Another solution is to call the power company and say, “I’m getting 130 volts out of the wall, and my light bulbs are lasting six weeks.” Sometimes they’ll send a guy to diagnose and help regulate it. We had big-time noise when we moved into the our building, and they came with some cool diagnostic equipment.
VG: What else?
RB: We should talk about old speakers. The formers (the round tube the voice coil is wound on) and the cones in old speakers are almost always dry-rotted and fractured. When you find that collectable old amp, be aware that the original speaker is going to expire within a few minutes when you crank it up. So it’s better to replace an original speaker and save it — and its original cone — for when some collector is going to pay you a fortune because the amp is all-original. You may get away with it for a while — but you’ve been warned! And luckily, there are many great re-coners out there.
VG: So, in summary….
RB: Remember that everything coming into and going out of an amp makes a difference in sound and quality of sound. A lot of guys don’t think about something as seemingly minor as electricity. But it makes a huge difference. And before you jump to a variac, you might want to get any old amp a tune-up. Sometimes just changing the caps and out-of-spec components can make a real difference in sound. The bottom line is finding a sound that turns you on and makes you play, because when you’re playing through an amp that really delivers, things come out of your fingers you didn’t even know were there!
David Jung is a professional writer/screenwriter and vintage guitar enthusiast living in Los Angeles, where he hangs with some of the best amp techs and collectors in town.
Source: https://mercurymagnetics.com/pages/news/VGmag/VGFeb08-RoyB.htm

 To honor and support the philanthropic efforts of legendary guitarist Eric Clapton, Fender is collaborating with Clapton to create a very special limited edition guitar and amp package featuring the new Eric Clapton Crossroads Stratocaster guitar and Crossroads ’57 Twin-Amp.
To honor and support the philanthropic efforts of legendary guitarist Eric Clapton, Fender is collaborating with Clapton to create a very special limited edition guitar and amp package featuring the new Eric Clapton Crossroads Stratocaster guitar and Crossroads ’57 Twin-Amp.
The Eric Clapton Crossroads Stratocaster guitar, or “Sun Strat” will be produced in a limited run of 100 instruments globally; the Crossroads ’57 Twin-Amps will number only 50. All profits from the project will benefit the Crossroads Centre, Antigua, the drug and alcohol addiction rehabilitation facility founded by Clapton on the small, idyllic Caribbean island in 1998.
Fifty of the guitars will be paired with the amps in exclusive Crossroads platinum packages for $30,000 each. The other 50 Crossroads guitars will be offered in packages for $20,000 each. The on-sale date is July 20, 2007 exclusively at www.fender.com—only eight days before Clapton’s monumental Crossroads Guitar Festival 2007 in Chicago on July 28.
While Fender has a long tradition of producing world-class signature series instruments with top musicians, this latest venture represents an extraordinary collaboration. Fender Custom Shop Master Builders have dedicated meticulous effort to reflect the spirit of Clapton’s artistry and philanthropy. Each guitar will be crafted to Clapton’s specification and bear a unique “Crossroads Antigua” graphic designed and originally hand-drawn by Clapton himself.

Fender’s Mike Eldred with an Eric Clapton
Crossroads Stratocaster and matching ’57 Twin-Amp
during taping of a segment for Chicago megastation WGN.
The commemorative Crossroads ’57 Twin-Amps are modeled after the original ’57 Twin — one of the most collectable amps of all time — with the classic Fender sound and design that made them so desirable. This limited-edition amplifier features a custom engraved commemorative “Crossroads 2007” badge autographed by Eric and his “Crossroads Antigua” graphic is artistically embedded on the grill cloth.
[Editor’s note: The amp’s Mercury Magnetics transformers and choke are exact clones of an exceptionally clean, vintage low-powered Tweed Twin from Fender’s private collection.]
“We are extremely honored to work with Eric on these limited edition Crossroads guitars and amps,” said Mike Eldred, Fender Custom Shop director. “At its essence, this is a passion project that allows Fender to support the Crossroads Centre, Antigua and to show our great love and appreciation for Eric.”
The Crossroads platinum package is highlighted by the Crossroads Edition ’57 Twin-Amp — the perfect sonic companion to the Crossroads guitar. The Fender ’57 Twin-Amp is Eric Clapton’s personal amp of choice for studio and stage use. This unique Crossroads premium package will also include a guitar certificate signed by Clapton; an official Crossroads tour laminate, set list and program book; Clapton guitar picks; a commemorative Crossroads guitar strap and a framed, limited edition art print of the Crossroads instrument package.
Fender has been known worldwide for half a century as a company with a spirit and tradition of pioneering innovation. That spirit and tradition is newly revitalized in this project, bringing together an incredible collaboration of passionate guitar players to create products to satisfy one of the ultimate guitar players of all time — Eric Clapton, an artist with his own tradition of pioneering innovation and social consciousness.

About Crossroads Guitar Festival 2007: Clapton’s Crossroads Guitar Festival 2007 takes place July 28 at Chicago’s Toyota Park, with a stellar lineup of blues and rock performers including Clapton, Jeff Beck, Sheryl Crow, Vince Gill, Buddy Guy, B.B. King, John Mayer, Willie Nelson, Steve Winwood and many others. The 28,000-capacity event sold out in only 15 minutes. As with the first Crossroads Guitar Festival, held in June 2004 in Dallas, proceeds from the concert benefit the Crossroads Centre, Antigua.
About Crossroads Centre, Antigua: Founded in 1998, Crossroads Centre, Antigua was created to provide treatment and education to chemically dependent persons, those with other compulsive addictive behaviors, their families and their significant others. Treatment is provided through residential care, family and aftercare programs. The pathway to recovery is founded on the movement toward a change in lifestyle. Crossroads Centre, Antigua also operates a 16-bed halfway house in Antigua called the Bevon House (exclusively for Antigua residents) and facilitates a school-based education series, Breaking the Cycle, in all Antiguan schools. The Crossroads Centre has recently expanded its program to offer transitional living for men, in line with the Crossroads Centre’s philosophy on recovery, at The Sanctuary in Delray Beach, Florida, for those who have completed a residential treatment program. For more information, visit www.crossroadsantigua.org.
For more information, visit: www.fender.com.
About Fender Musical Instruments Corporation: Fender Musical Instruments Corporation (FMIC) is the world’s foremost manufacturer of guitars, amplifiers and related equipment since 1946, and its name has become synonymous with all things rock ‘n’ roll. Iconic Fender® instruments such as the Telecaster®, Stratocaster®, Precision Bass® and Jazz Bass® guitars are known worldwide as the instruments that started the rock revolution, and they continue to be highly prized by today’s guitarists and collectors. FMIC brands include Fender®, Squier®, Guild®, Gretsch®, Jackson®, Charvel®, SWR®, EVH®, Tacoma®, Olympia® and Brand X®.
Fender Crossroads Specialty Site: www.fender.com/crossroads.
Source: https://mercurymagnetics.com/pages/news/GuitarPlayer/GPJun07.htm
Tweed — 50V bias tap — lower B+ — 325-0-325
Tweed — lowest B+ — 250-0-250
Tweed — Model 5E5-A — with bias tap
Mid ’50s Tweed – 5E4-A — two 6V6 tube version — lower B+ — 335-0-335
Tweed — Model 5E5-A — with bias tap — 220V, 230V & 240V primary
Tweed
Tweed
Tweed era — 3.5 Henry — #14684 Small size — 2 13/16″ mounting centers
3H — 150mA
Tweed — #45216 — single 4 ohm tap — 3 9/16″ mounting centers
Tweed — 2, 4 & 8Ω taps
Tweed — 5D4 — no CT on 6.3V
Tweed — 5D4 — no CT on 6.3V — 220V, 230V & 240V primary
Tweed — 4 Henry. Uses Grain-Oriented Iron
3.5H / 200mA Choke — Fender Tweed Era Part #14684 — Small size — 2 13/16″ Mounting Centers
Tweed era — 3.5 Henry — #14684 Small size — 2 13/16″ mounting centers
Tweed (very early 1947) — single 8Ω tap
4H / 500mA Choke — Fender Tweed era Part # 14684
Large vertical mount — 3 1/8″ center to center — for Bassman amps (not Champ)
Mid ’50s Tweed — single 8Ω tap — 2″ mounting center
Mid ’50s Tweed — single 4Ω tap — 2″ mounting center — medium size version
Late ’50s Tweed — single 4Ω tap — 2-3/8″ mounting center — largest version
Tweed — 8Ω tap
Early ’50s Tweed — single 4Ω tap — 1-3/4″ mounting center — smallest version
Tweed — 4, 8 & 16Ω taps
10H Tweed Era Choke — 2 13/16″ mounting centers — DCR: 192 ohms
50’s Tweed Era — 5 H / 40mA
53 Tweed — Mounts to the speaker frame! — exact clone from a 1953 Princeton
’55 Tweed – 4Ω tap
’55 Tweed — 8Ω tap
The “White” amp — rare version from 1956 — single 4Ω tap
(Similar amp to Tweed Princeton)
’60 Tweed — 8Ω tap
’60 Tweed — 8Ω tap
Late ’50s Tweed — #50246 — 8 kΩ primary, single 8 ohm tap
Secondary has self leads like original — Horizontal frame — 3 1/8″ mounting centers
Late ’50s Tweed — #50246 — 8 kΩ primary, single 8 ohm tap
Secondary has self leads like original — Horizontal frame — 3 1/8″ mounting centers
Late ’50s Tweed — #108
Early ’50s Tweed — #1848
Larger size — Tweed era — 3.5 Henry — 3 1/8″ Mounting Centers
Tweed — 4Ω tap — #1848
Tweed — 2, 4 & 8Ω taps
Single 8Ω tap — 8k primary — Oversized Upgrade!
Tweed — 2, 4 & 8Ω taps
50s Tweed — #1848 — dual self leads — Uses Grain-Oriented Iron
Early Tweed — vertical mount — 6K primary — 8Ω secondary — #1846
’55 Tweed
’55 Tweed — 240V primary
Tweed — #1846 — single 8Ω secondary
Tweed — single 2.6Ω tap — Triad #1846
59 Tweed — 330-0-330 — NO CT on the 6.3V winding — 5V winding
Tweed — 220V, 230V & 240V primary
’60 Tweed — #66079, #125P1B — flat mount type, 1 1/4″ tall lamination stack
Bolt hole spacing 2″ x 2 1/2″
’60 Tweed — Single 100V primary — higher B+
Tweed — #125P6A
Late ’50s Tweed
’59 Tweed — 220V, 230V & 240V primary
Tweed — 100V & 120V primary
Mid ’50s Tweed — 260-0-260 — CT on the 6.3V winding — 5V winding
Late ’50s Tweed — Universal Voltage Primary
Tweed — Universal Voltage Primary — lower B+
Tweed — Universal Voltage Primary
Tweed — used on original late ’40s Pro — 10 Henry — very large size — four screw mount
’59 Tweed — #45249 — single 2Ω secondary — bolt hole spacing w/ L-bkts is 2 1/4″ x 3 1/8″
Optional “Especial” bracket is 2″ x 3 3/8″
’59 Tweed — 2 & 4Ω taps
’59 Tweed — 2, 4 & 8Ω taps
’59 Tweed — 4 kΩ primary — 4, 8 & 16Ω taps
Bolt hole spacing w/ “Especial” bracket is 2″ x 3 3/8″ (L-bkts is 2 1/4″ x 3 1/8″)
’59 Tweed — 4 & 8Ω taps
’57 Tweed — smaller size — #2485
’57-’59 Tweed — lower B+ — #8160
’57-’59 Tweed — #8160
Low Power Tweed — #2818
Low Power Tweed — 4, 8 & 16Ω taps
’55-’60 Tweed — lower B+ — 100V, 120V, 220V, 230V & 240V primary
Tweed — 2.6Ω tap — **Fat Stack version, check fit before ordering.
Bolt hole spacing is 2 1/2″ x 3 3/8″
’59 Tweed — 2, 4, 8 & 16Ω taps — UL taps
’59 Tweed — lower B+
Tweed — 8Ω tap
Tweed — 2Ω tap
59 Tweed — Triad 8087 size — same as ’58 — with separate, insulated bias winding
Tweed (very early 1947) — #45166
Tweed — Triad #8087
58 Tweed — Triad 8087 size — same as ’59 — with bias tap coming off B+ winding
Tweed — EARLY #6516 — Model 5E5 — no bias tap — no CT on 6.3V — self leads on 6.3V & 5V
’58 Tweed — 100V, 120V, 220, 230V & 240V primary
’58 Tweed — lower B+ — 100V, 120V, 220, 230V & 240V primary
Low Power Tweed — 5C8 & 5D8 — smaller size — no CT on 6.3V winding
High Power Tweed — #7993 — slightly higher B+
High Power Tweed — #7993
’57 Tweed — #7993
Low Power Tweed Twin PT — 120V
High Power Tweed — 240V primary
59 Tweed — lowest B+ — 100V, 120V, 220V, 230V & 240V primary
’59 Tweed — lower B+ — 220V, 230V & 240V primary
High Power Tweed — 2 & 4Ω taps
59 Tweed — with separate, insulated bias winding — 100V, 120V, 220V, 230V & 240V primary
’59 Tweed
’59 Tweed — Universal Voltage Primary
59 Tweed — 275-0-275 unloaded B+ — separate bias winding
59 Tweed — 275-0-275 unloaded B+ — separate bias winding — 220V, 230V & 24V primary
’59 Tweed — lowest B+
Tweed — #6516 — Model 5E5 — no bias tap
Tweed — Lower B+ — 230V & 240V primary
Tweed — Lower B+ — Universal Voltage Primary
Tweed — Lower B+
Tweed — higher B+
High Power Tweed — #45268 with 4 Ohm Secondary
’55 Tweed — bias tap — #7993
High Power Tweed — 4, 8 & 16Ω taps
’57 Tweed — #7993 — Universal Voltage Primary
High Power Tweed Twin — true balanced center tap on 6.3V filament winding –Uses Grain-Oriented Iron
Tweed GA-14 Titan
4K primary — single 8 Ohm Secondary
Tweed — single 8 Ohm tap
Tweed — 4, 8 & 16 Ohm taps
Tweed — 4, 8 & 16 Ohm taps
8k primary — 8 and 16 Ohm secondary
Early 5C8/5D8 Narrow Panel Tweed — #2485 — 8k primary with single 4 Ohm secondary
Tweed — 4, 8 and 16 Ohm Secondary
Mid ’50s Tweed – 5E4-A — two 6V6 tubes — single 8 Ohm tap
Single 8 Ohm tap — 8k primary
Tweed — single 8 Ohm tap — oversized
Tweed — single 4 Ohm tap — oversized
4, 8 & 16 Ohm taps — 8k primary — Oversized Upgrade!
4, 8 & 16 Ohm taps — 8k primary — Oversized Upgrade!
Mid ’50s Tweed – 5E4-A — two 6V6 tubes — single 4 Ohm tap
Low Power Tweed Twin — smaller size — 230 & 240V primary
Tweed — single 2 Ohm tap
Tweed — 4 & 8 Ohm taps
Tweed 3×10 — single 2.6 Ohm tap — two screw, A frame style
Low Power Tweed Twin — 220, 230 & 240V primary
59 Tweed — 330-0-330 — Center Tapped Filament Wind — 5V winding
Tweed — 4, 8 and 16 Ohm Secondary — Oversized Upgrade!
Tweed Era — 4, 8 and 16 Ohm Taps
Mid ’50s Tweed – 5E4-A — two 6V6 tube version — Lower B+ — 335-0-335VAC Unloaded — With Universal Voltage Primary
’59 Tweed — Lower B+ — with Universal Voltage Primary
Low Power Tweed Twin — With Universal Voltage Primary
Tweed — 4 and 8 Ohm Secondary — #1848